Foods That Disrupt Our Microbiome
Eating a diet filled with animal products can disrupt our microbiome faster than taking an antibiotic. If you search online for “Crohn’s disease and diet” […]

Eating a diet filled with animal products can disrupt our microbiome faster than taking an antibiotic.
If you search online for “Crohn’s disease and diet” or “ulcerative colitis and diet,” the top results are a hodgepodge of conflicting advice, as you can see below and at 0:15 in my video Preventing Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Diet.
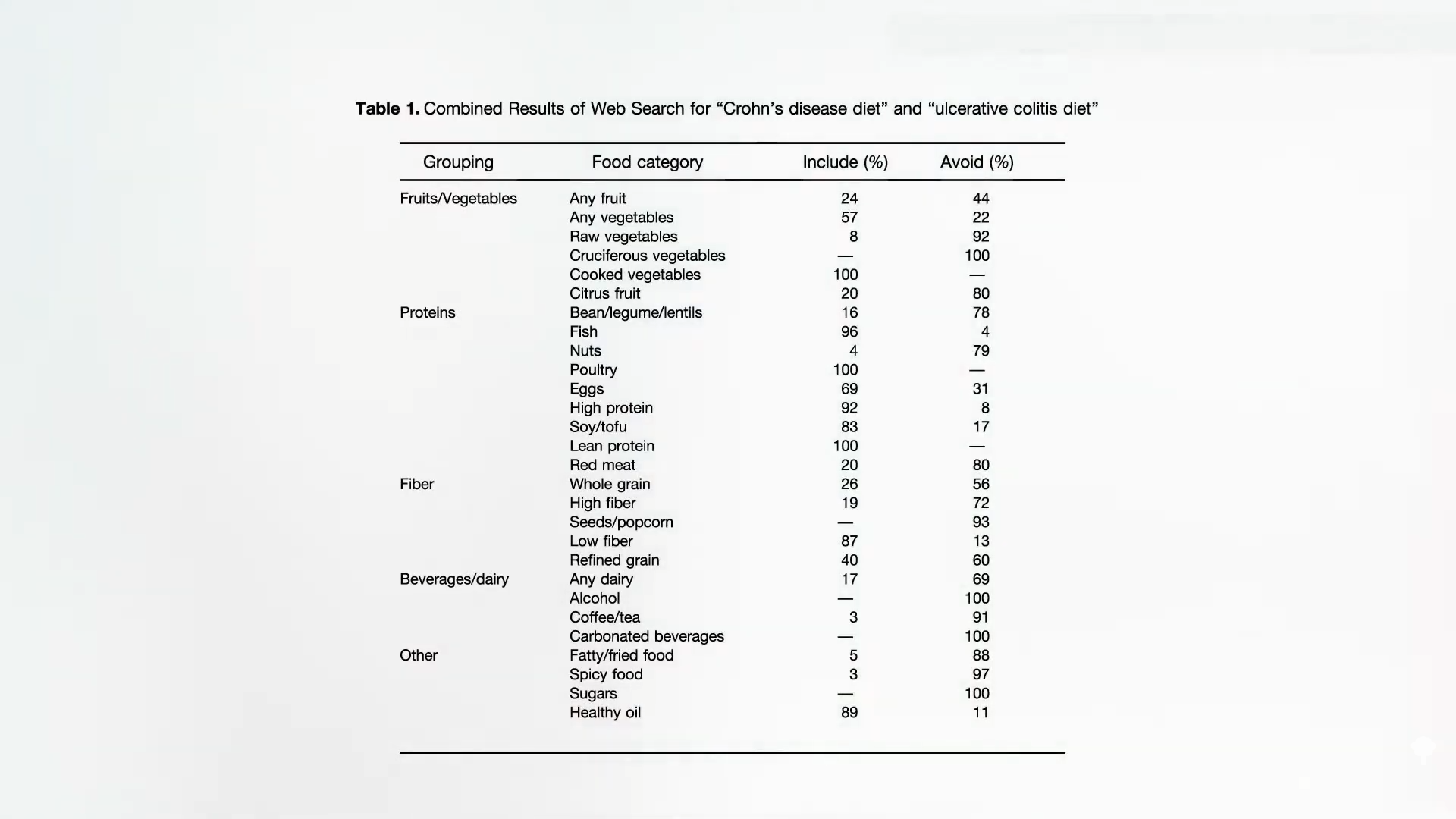
What does science say? A systematic review of the medical literature on dietary intake and the risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease finds that Crohn’s disease is associated with the intake of fat and meat, whereas dietary fiber and fruits appear protective. The same associations are seen with ulcerative colitis, the other major inflammatory bowel disease—namely, increased risk with fat and meat, and a protective association with vegetable intake.
Why, according to this meta-analysis of nine separate studies, do meat consumers have about a 50 percent greater risk for inflammatory bowel disease? One possibility is that meat may be a vehicle for bacteria that play a role in the development of such diseases. For instance, meat contains “huge amounts of Yersinia.” It’s possible that antibiotic residues in the meat itself could be theoretically mucking with our microbiome, but Yersinia are so-called psychotropic bacteria, meaning they’re able to grow at refrigerator temperatures, and they’ve been found to be significantly associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This supports the concept that Yersinia infection may be a trigger of chronic IBD.
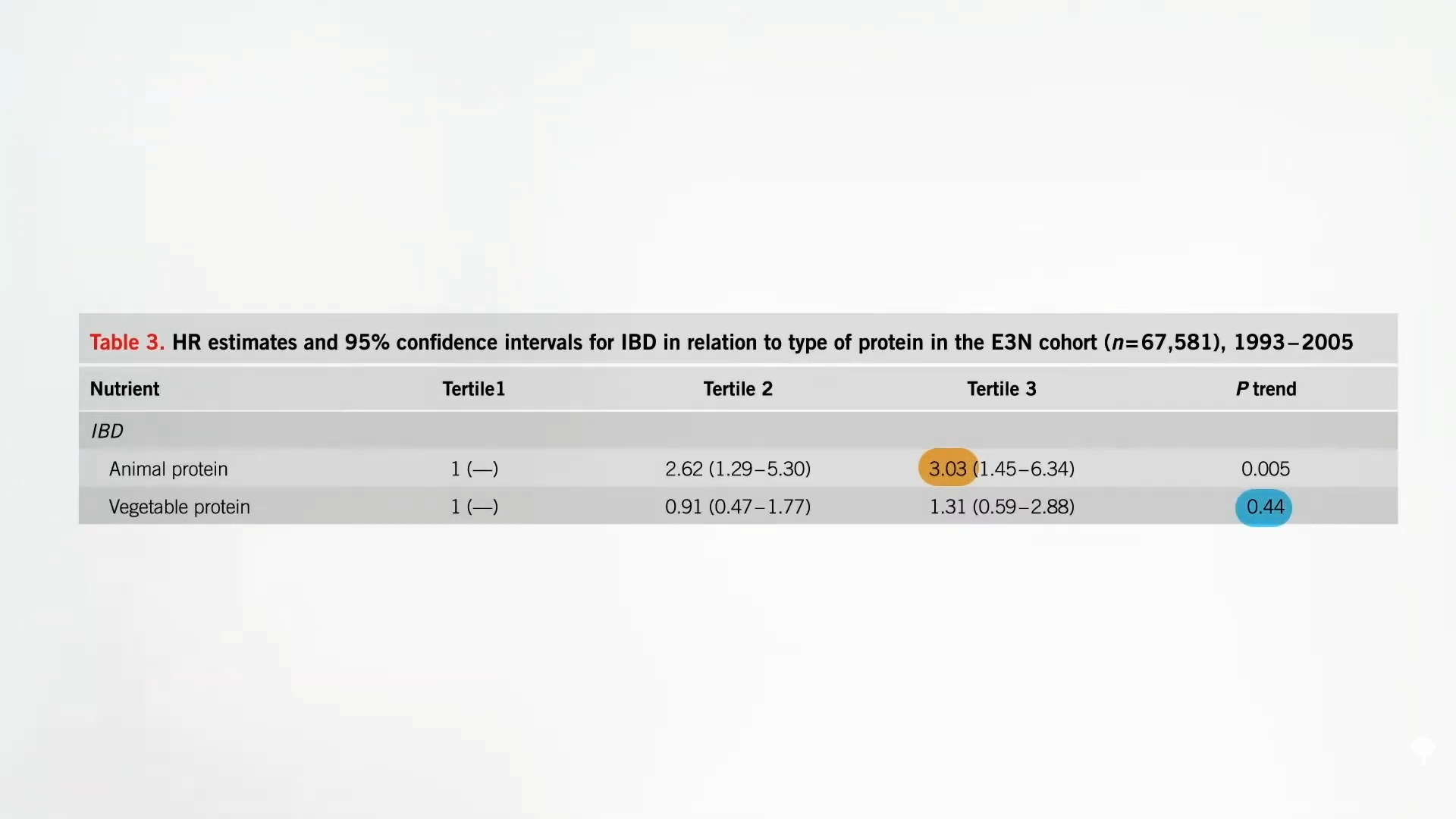
Animal protein is associated with triple the risk of inflammatory bowel disease, but plant protein is not, as you can see below and at 1:39 in my video. Why? One reason is that animal protein can lead to the formation of toxic bacterial end products, such as hydrogen sulfide, the rotten egg gas. Hydrogen sulfide is not just “one of the main malodorous compounds in human flatus”; it is a “poison that has been implicated in ulcerative colitis.” So, if you go on a meat-heavy, low-carb diet, we aren’t talking just about some “malodorous rectal flatus,” but increased risk of irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel syndrome (ulcerative colitis), and eventually, colorectal cancer.
Hydrogen sulfide in the colon comes from sulfur-containing amino acids, like methionine, that are concentrated in animal proteins. There are also sulfites added as preservatives to some nonorganic wine and nonorganic dried fruit, but the sulfur-containing amino acids may be the more important of the two. When researchers gave people increasing quantities of meat, there was an exponential rise in fecal sulfides, as seen here and at 2:37 in my video.
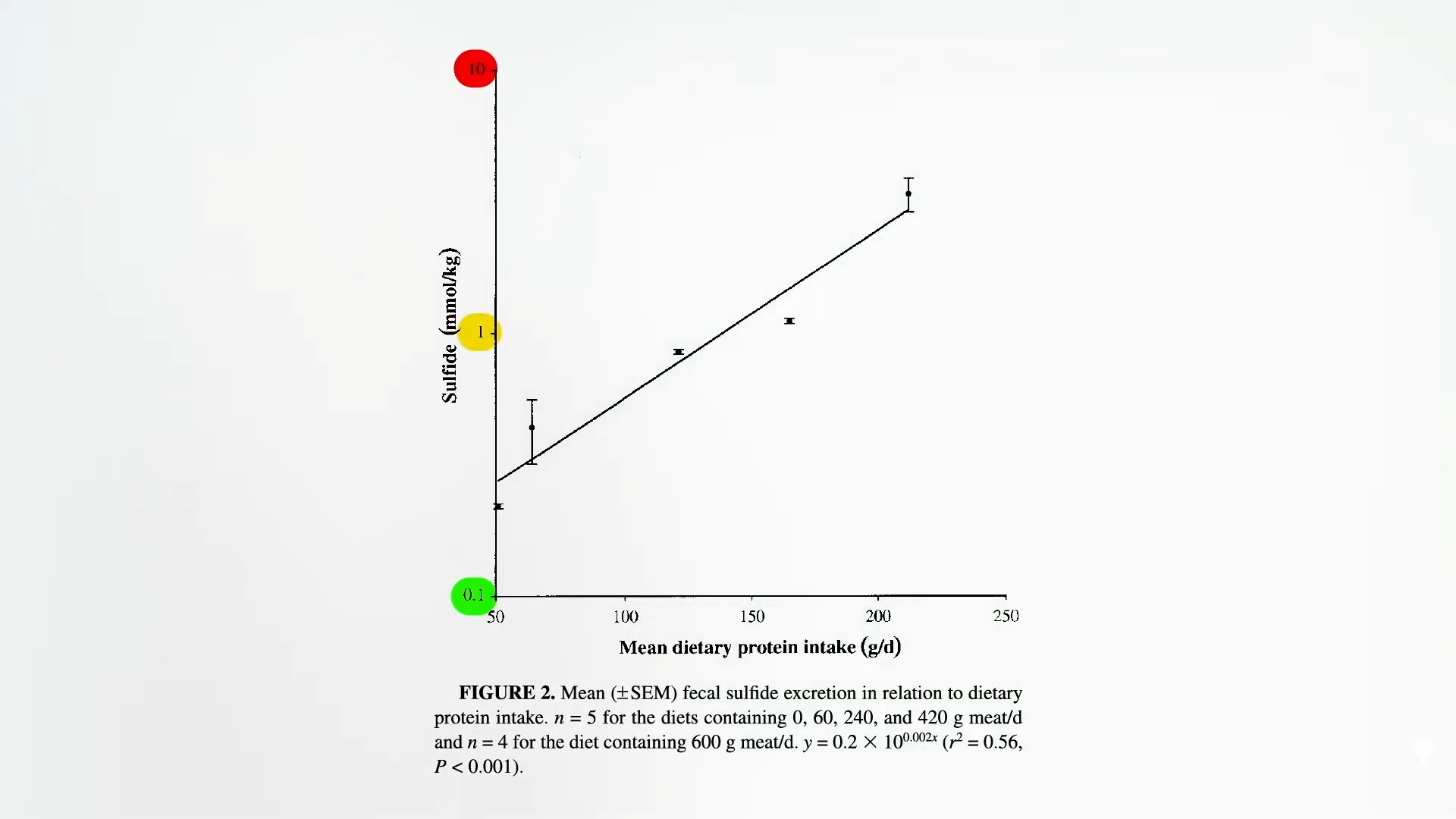
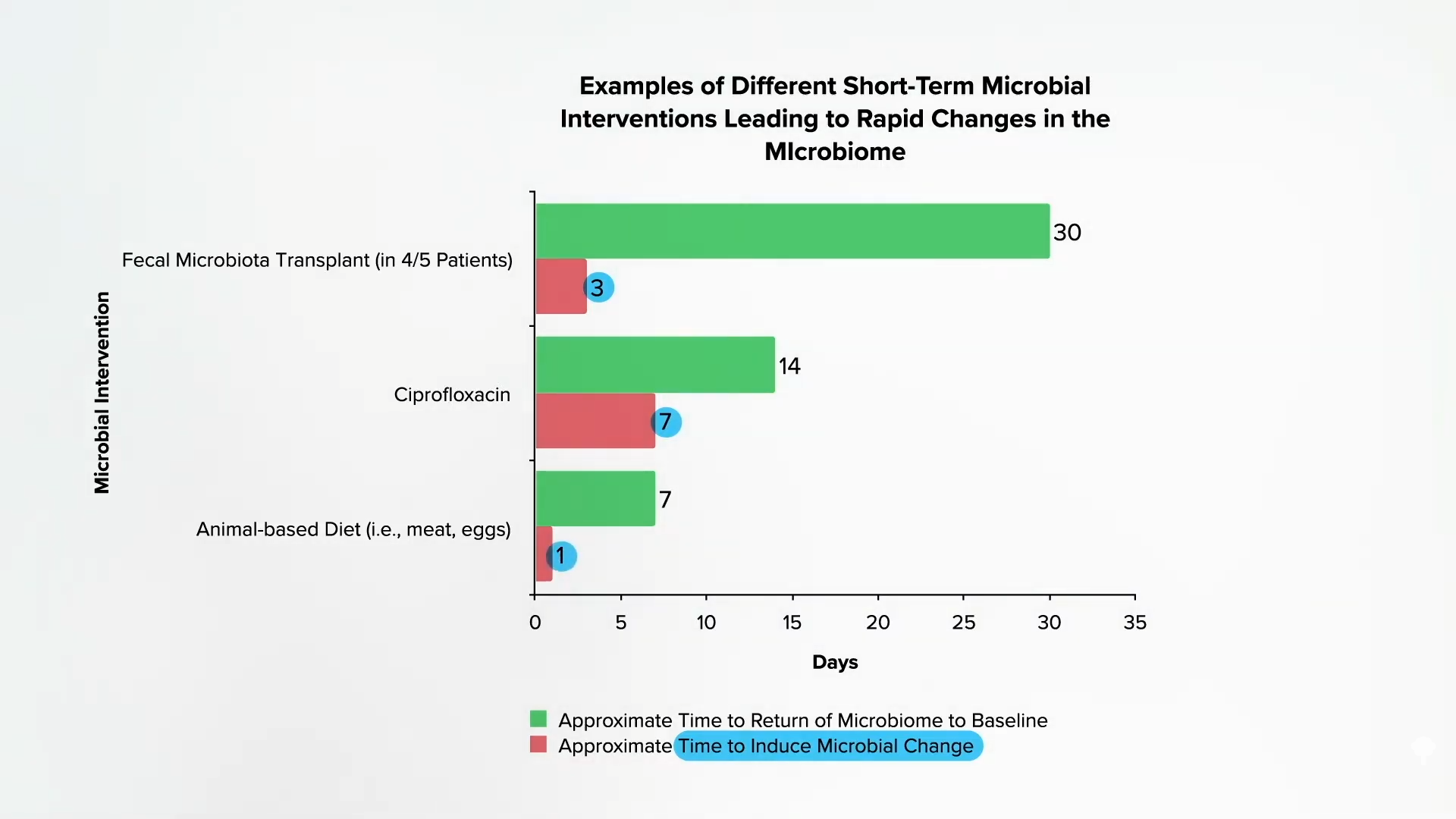
Specific bacteria, like Biophilia wadsworthia, can take this sulfur that ends up in our colon and produce hydrogen sulfide. Eating a diet based on animal products, packed with meat, eggs, and dairy, can specifically increase the growth of this bacteria. People underestimate the dramatic effect diet can have on our gut bacteria. As shown below and at 3:12 in my video, when people are given a fecal transplant, it can take three days for their microbiome to shift. Take a powerful antibiotic like Cipro, and it can take a week. But if we start eating a diet heavy in meat and eggs, within a single day, our microbiome can change—and not for the better. The bad bacterial machinery that churns out hydrogen sulfide can more than double, and this is consistent with the thinking that “diet-induced changes to the gut microbiota [flora] may contribute to the development of inflammatory bowel disease.” In other words, the increase in sulfur compounds in the colon when we eat meat “is not only of interest in the field of flatology”—the study of human farts—“but may also be of importance in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis…”
Doctor’s Note:
This is the first in a three-part video series. Stay tuned for The Best Diet for Ulcerative Colitis Treatment and The Best Diet for Crohn’s Disease Treatment.