ML DAY 2 GIT ADVANCE COMMANDS
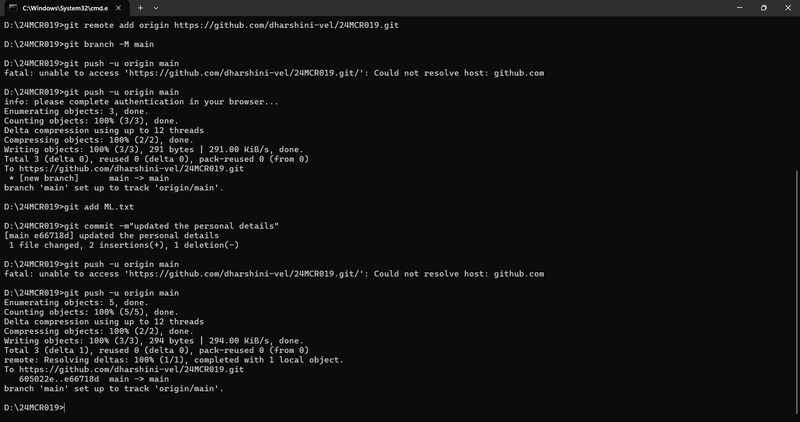
1.The git diff command in Git is used to show the difference between changes in your code. It helps you see what has been added, modified, or deleted before you commit. 2.The git log command shows the commit history of your Git repository. It’s like a timeline of all the changes made in your project. 3.The git clone command is used to create a local copy of a remote Git repository. It downloads the entire repository including all files, branches, and commit history. Syntax: git clone https://github.com/username/repo-name.git This creates a new folder named repo-name and puts the cloned repo inside. The git fork is not a Git command you run in your terminal — it's a concept used mostly on platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. What is a Fork? A fork is a copy of someone else’s repository under your own account, usually done through a Git hosting service (like GitHub). It's often used when you want to: Propose changes to someone else's project (via pull requests). How to Fork (on GitHub): Go to the repository you want to fork. Click the "Fork" button in the top-right corner. GitHub will copy that repo to your own GitHub account. 5.The git pull updates your local branch with the latest changes from the remote repository. 6.The git push uploads your committed changes from your local branch to a remote branch. Syntax: git push origin branch-name
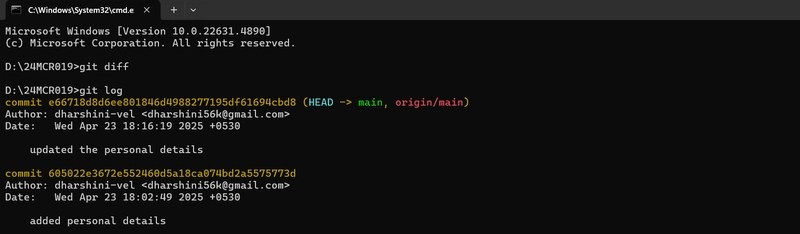
1.The git diff command in Git is used to show the difference between changes in your code. It helps you see what has been added, modified, or deleted before you commit.
2.The git log command shows the commit history of your Git repository. It’s like a timeline of all the changes made in your project.
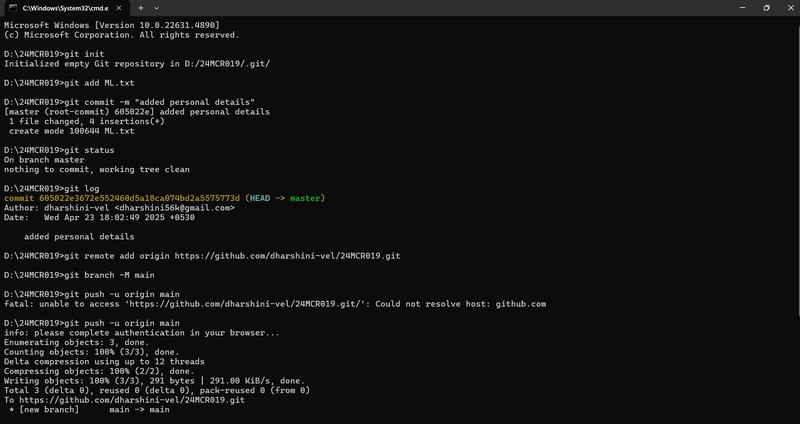
3.The git clone command is used to create a local copy of a remote Git repository. It downloads the entire repository including all files, branches, and commit history.
Syntax:
git clone https://github.com/username/repo-name.git
This creates a new folder named repo-name and puts the cloned repo inside.
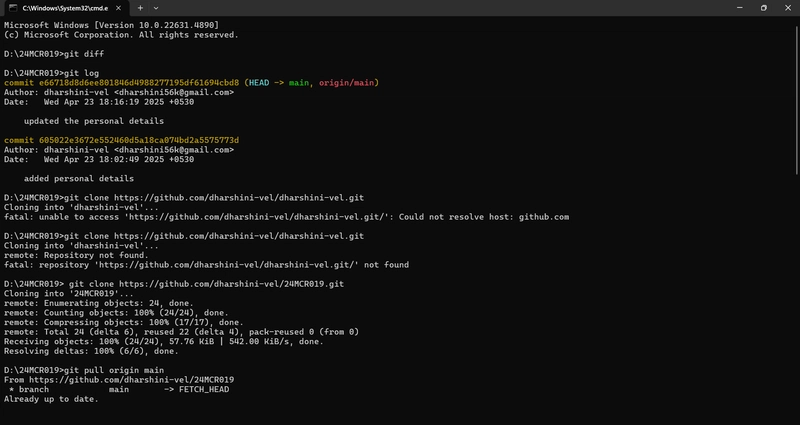
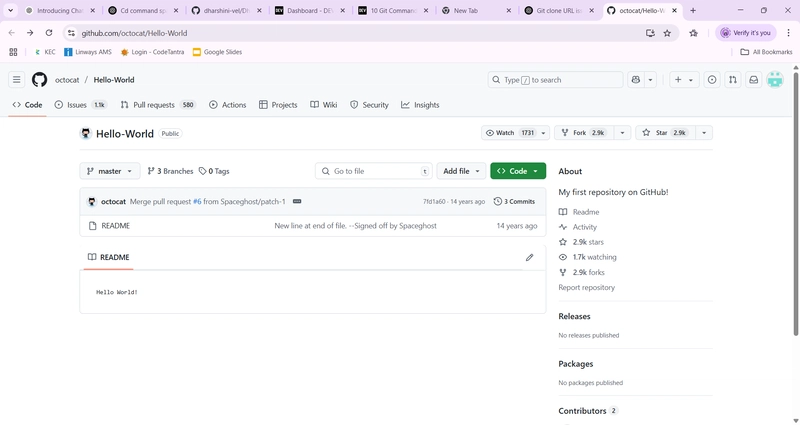
The git fork is not a Git command you run in your terminal — it's a concept used mostly on platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
What is a Fork?
A fork is a copy of someone else’s repository under your own account, usually done through a Git hosting service (like GitHub). It's often used when you want to:
Propose changes to someone else's project (via pull requests).
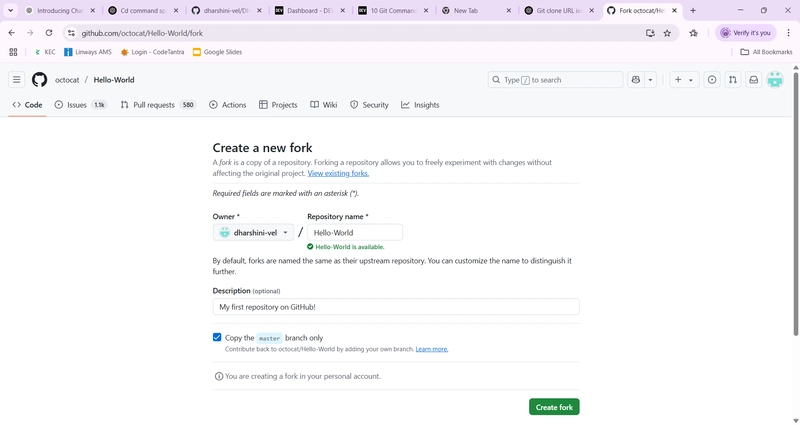
How to Fork (on GitHub):
Go to the repository you want to fork.
Click the "Fork" button in the top-right corner.
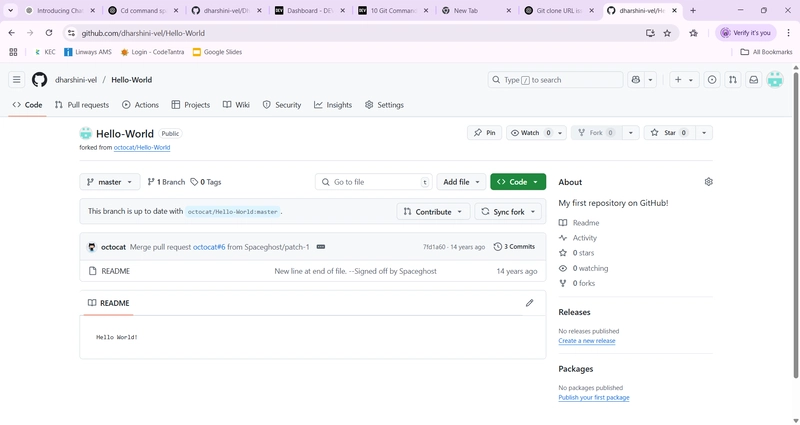
GitHub will copy that repo to your own GitHub account.
5.The git pull updates your local branch with the latest changes from the remote repository.
6.The git push uploads your committed changes from your local branch to a remote branch.
Syntax:
git push origin branch-name