How to Write Effective Prompts for AI Agents using Langbase
Prompt engineering isn’t just a skill these days – it gives you an important competitive edge in your development. In 2025, the difference between AI agents that work and those that don’t comes down to how well they’re prompted. Whether you’re a deve...

Prompt engineering isn’t just a skill these days – it gives you an important competitive edge in your development.
In 2025, the difference between AI agents that work and those that don’t comes down to how well they’re prompted. Whether you’re a developer, product manager, or just building with AI, getting really good at prompt engineering will make you significantly more effective.
Langbase lets you craft high-performance prompts and deploy serverless AI agents optimized for the latest models. In this article, we’ll break down tips and tricks to help you design effective prompts. We’ll also look at some advanced prompt engineering techniques for building serverless agents, and how to fine-tune LLM parameters to get the best results.
Prerequisites
To get the most out of this article, you’ll need:
A Langbase account – Sign up on Langbase if you haven’t already.
Basic knowledge of LLMs, AI agents, and RAG (retrieval-augmented generation).
Here’s what I’ll cover:
Let’s get started!
Prompt Engineering Fundamentals
A prompt tells the AI what to do—it sets the context, guides the response, and shapes the conversation. Prompt engineering is about designing prompts that make AI agents actually useful in real-world applications.
Here’s how to write good prompts:
1. Define your goal clearly
Before crafting a prompt, be clear about what you want to achieve—just like planning logic before writing code. Consider whether dynamic inputs are needed and how they’ll be handled. Define the ideal output format, whether JSON, XML, or plain text. Determine if the model requires additional context or if its training data is enough.
Set any constraints on response length, structure, or tone. Fine-tune LLM parameters if necessary to improve control. The more precise your goals, the better the results. And remember, effective prompt engineering is often a team effort.
Here’s an example prompt to help you out. If you're building a customer support bot, your goal should look like this:
"Generate concise, polite responses in plain text, pulling details from the company knowledge base."
Define the output format (JSON, XML, plain text).
- Example: "Respond in JSON format with 'answer' and 'source' fields."
Decide if extra context is needed.
- Example: "Use this document as reference: [URL]."
Set constraints on length, tone, or structure.
- Example: "Limit response to 50 words, use a friendly tone."
2. Experiment relentlessly
LLMs aren’t perfect, and neither is prompt engineering. Test everything. Try different formats, tweak parameters, and provide examples. AI models vary in capability—refining prompts through iteration is the only way to ensure reliable outputs.
Suppose your AI isn’t giving useful answers. You could:
Rephrase the prompt: Instead of "Explain this topic," try "Summarize this in one paragraph with key takeaways."
Add constraints: "Limit response to three bullet points."
Give examples: "For example, if asked about Python, reply like this: 'Python is a versatile language used for AI, web development, and automation.'”
3. Treat LLMs like machines, not humans
LLMs don’t think. They follow instructions—precisely. Ambiguity confuses them. Over-explaining can be just as bad as under-explaining. And remember: LLMs will generate an answer, even if it’s wrong. You have to manage this risk.
Here’s a comparison between over and under-explaining prompts:
Over-explaining: "Can you please, if possible, provide a very detailed yet concise explanation about how neural networks work, but not too technical, and try to be engaging, but also keep it short?"
Better prompt: "Explain neural networks in simple terms, under 100 words, with an analogy."
Under-explaining: "Tell me about neural networks."
Better prompt: "Describe neural networks in two sentences with an example."
Tips and Tricks for Effective Prompt Design
Here are a few tips and tricks to help you effectively prompt engineer your AI and agents:
Be specific – Vague prompts lead to bad outputs. Define the format, tone, and level of detail you want. If needed, break complex tasks into smaller steps and chain your prompts.
Control response length – If you need a concise response, specify the word or character limit. For example: “Summarize this in 50 words.”
Provide context – LLMs don’t know everything. If the model needs specific knowledge, include it in your prompt. For dynamic context, use a RAG-based approach to inject relevant information on demand.
Use step-by-step reasoning – If a task requires logical reasoning, instruct the model explicitly: “Think step by step before answering.” This improves accuracy.
Separate instructions from context – Long prompts can get messy. Start with clear instructions, then separate additional info.
Tell it what to do, not what to avoid – Instead of saying, “Don’t explain the answer,” say, “Only output the final answer.” Positive instructions work better.
Set constraints – Define limits on tone, length, or complexity. Example: “Write in a professional tone, under 3 sentences.”
Assign a role – LLMs perform better with a defined persona. Start with, “You are an expert in X,” for example, to guide the model’s behavior.
Use examples – If precision matters, show the model what you expect. Techniques like few-shot and chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting help improve complex reasoning.
Langbase Pipe Agent Prompts
AI agents aren’t just chatbots—they reason, plan, and take action based on user inputs. Unlike simple LLM queries, AI agents operate autonomously, making decisions and interacting with external tools to complete tasks.
Langbase Pipe Agents are serverless AI agents with unified APIs for every LLM. They let developers define structured prompts to control agent behavior across different models. In this section, you'll learn how to structure prompts effectively by creating an AI agent Pipe to get reliable and useful responses.
The three key prompts in Langbase Pipe agents
To make AI agents work effectively, you need three types of prompts:
System prompt: Defines the LLM model's role, tone, and guidelines before processing user input.
User prompt: The input given by the user to request a response from the model.
AI assistant prompt: The model's generated response based on the user’s input.
To learn how to use these three prompts with the UI using Langbase AI studio, you’ll find clear and concise instructions in this guide. It explains exactly where to go/what to click to write these prompts.
Let’s learn how to create an AI agent Pipe using the Langbase AI studio:
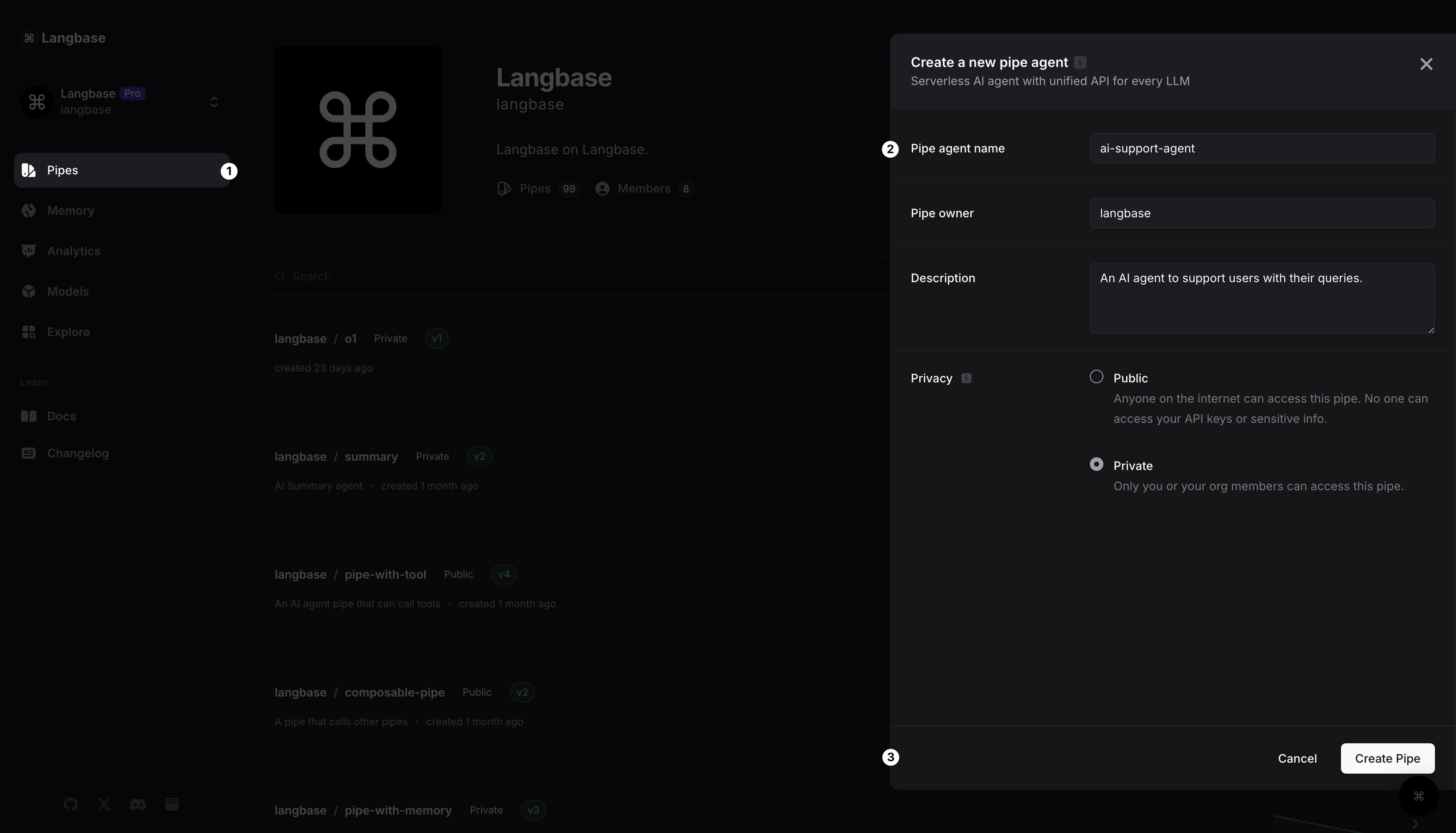
Step 1: Create a Pipe agent
After logging into your Langbase account, you can always go to pipe.new to create a new Pipe.
Give your Pipe a name. Let’s call it
AI support agent.Click on the
[Create Pipe]button. And just like that, you have created your first Pipe.
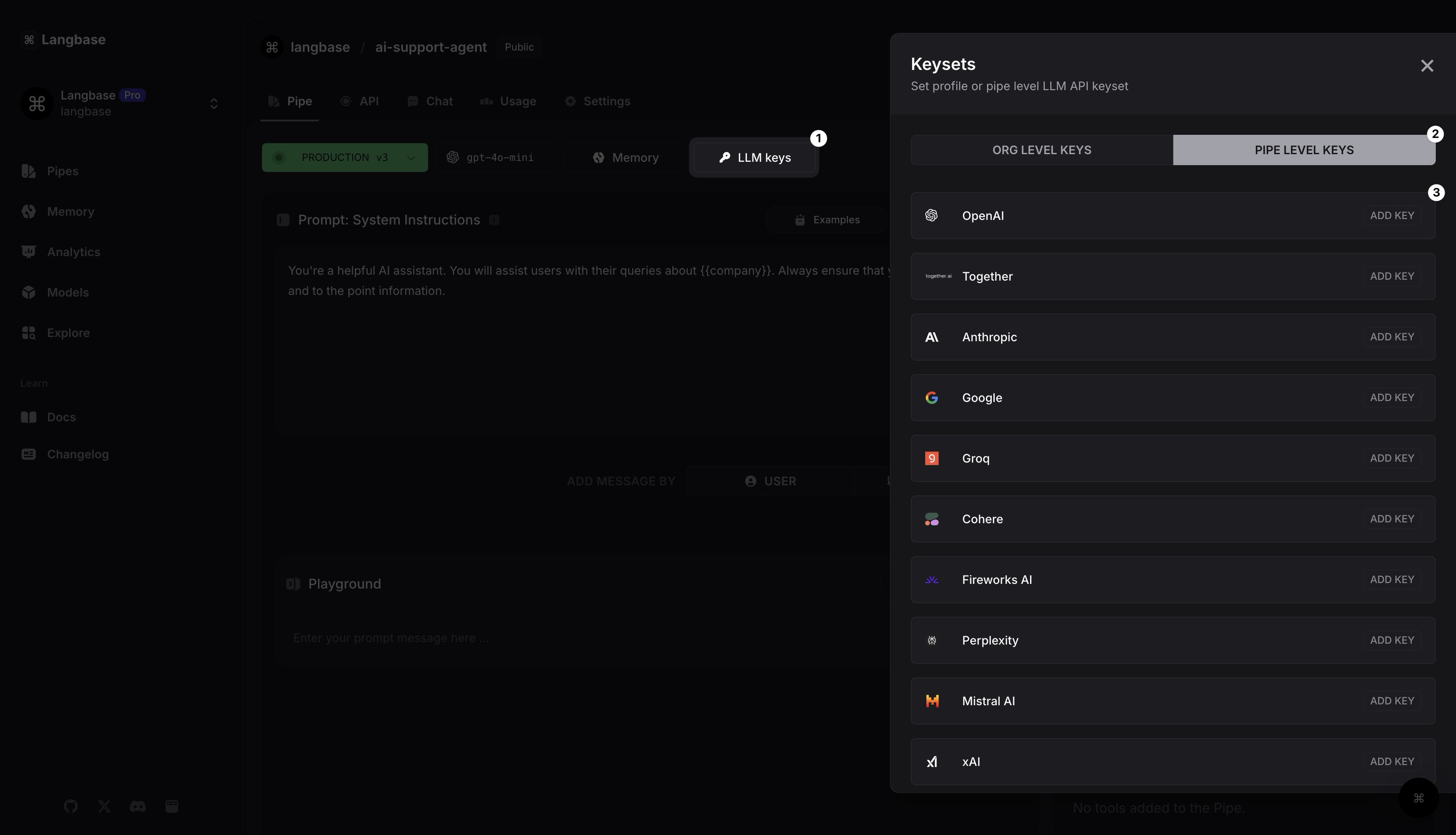
Step 2: Using an LLM model
If you have set up LLM API keys in your profile, the Pipe will automatically use them. If not, just hit the LLM API Keys button or head over to Settings to add Pipe-level LLM API keys.
Let's add an LLM provider API key now.
Click on the LLM keys button. It will open a side panel.
Select Pipe level keys. Choose any LLM. For example, you can use
OpenAI(for GPT) or any other 250+ supported models on Langbase.Click on OpenAI
[ADD KEY]button, add your LLM API key. Inside each key modal, you'll find a linkGet a new key from hereclick it to create a new API key on any API provider's website.
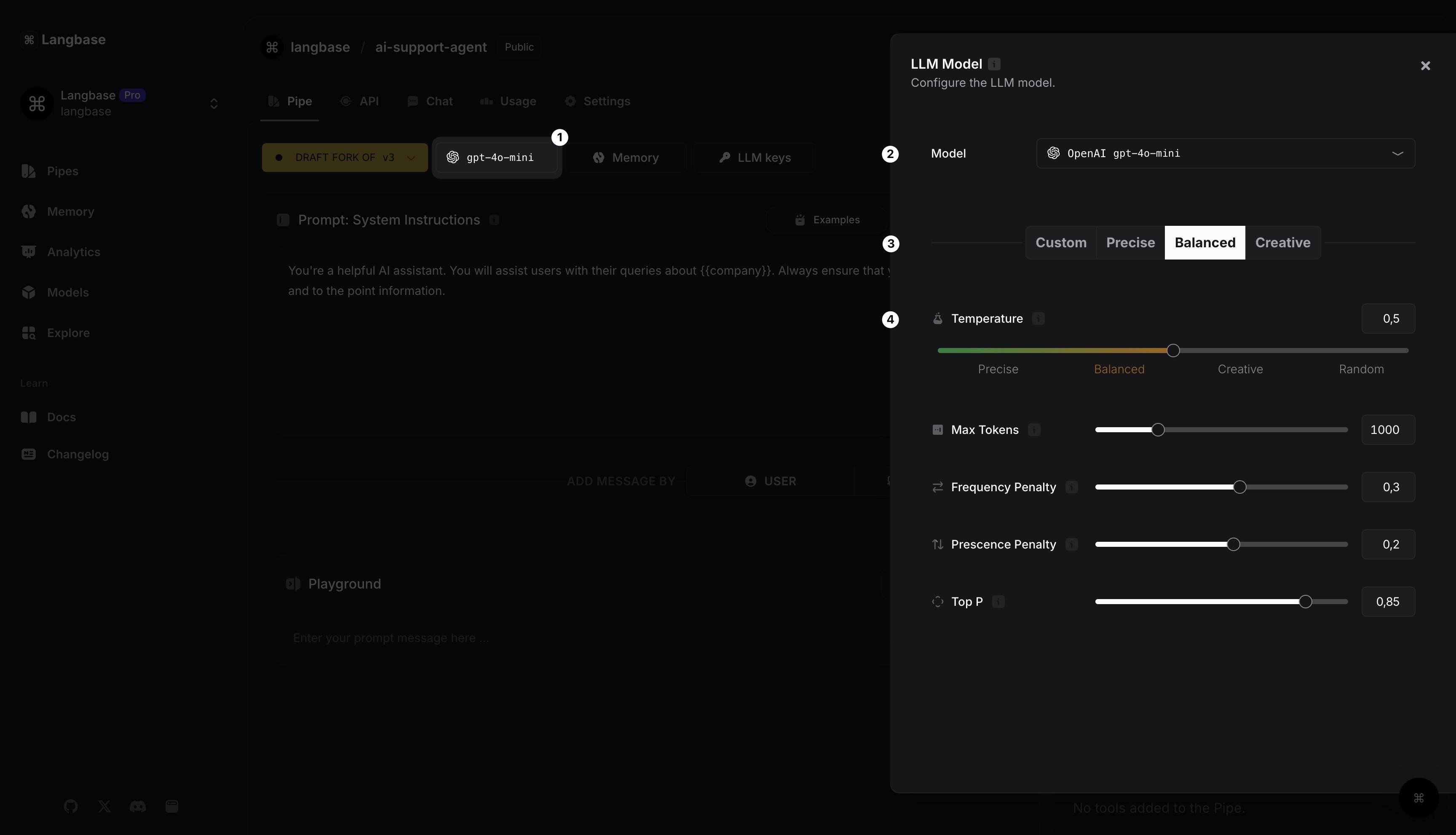
Step 3: Build your Pipe: Configure LLM model
Let's start building our pipe. Go back to the Pipe tab and follow these steps:
Click on the
gpt-4o-minibutton to select and configure the LLM model for your Pipe.By default OpenAI
gpt-4o-miniis selected. You can also pick any LLM model.Choose one of the pre-configured presets for your model.
You can also modify any of the model params. Learn more with the icon, next to param name.
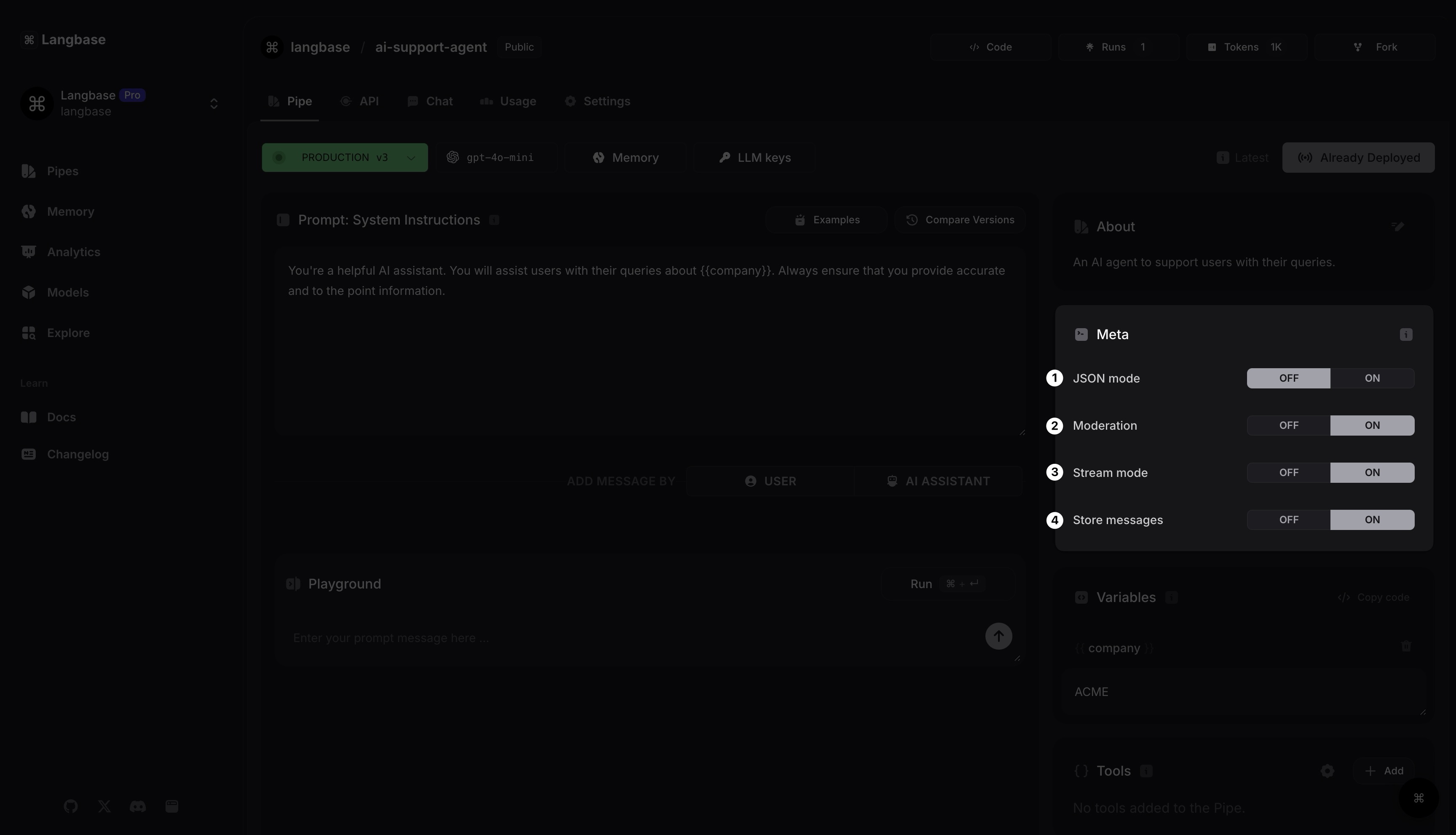
Step 4: Build your Pipe: Configure the Pipe's Meta
Use the Meta section to configure how your AI support agent Pipe should work. There are multiple ways you can configure it.
To start, you can set the output format of the Pipe to JSON. You can also turn on moderation mode to filter out inappropriate content as a requirement by OpenAI.
Then you can turn the streaming mode on and off, and turn off storing messages (input prompt and generated completion) for sensitive data like emails.
Step 5: Design a Prompt
Now that you have your LLM model and Pipe meta configured, it's time to design your prompt.
Prompt: System Instructions
Let's add a system instruction message to this agent. You can add this: You're a helpful AI assistant. You will assist users with their queries about {{company}}. Always ensure that you provide accurate and to the point information.
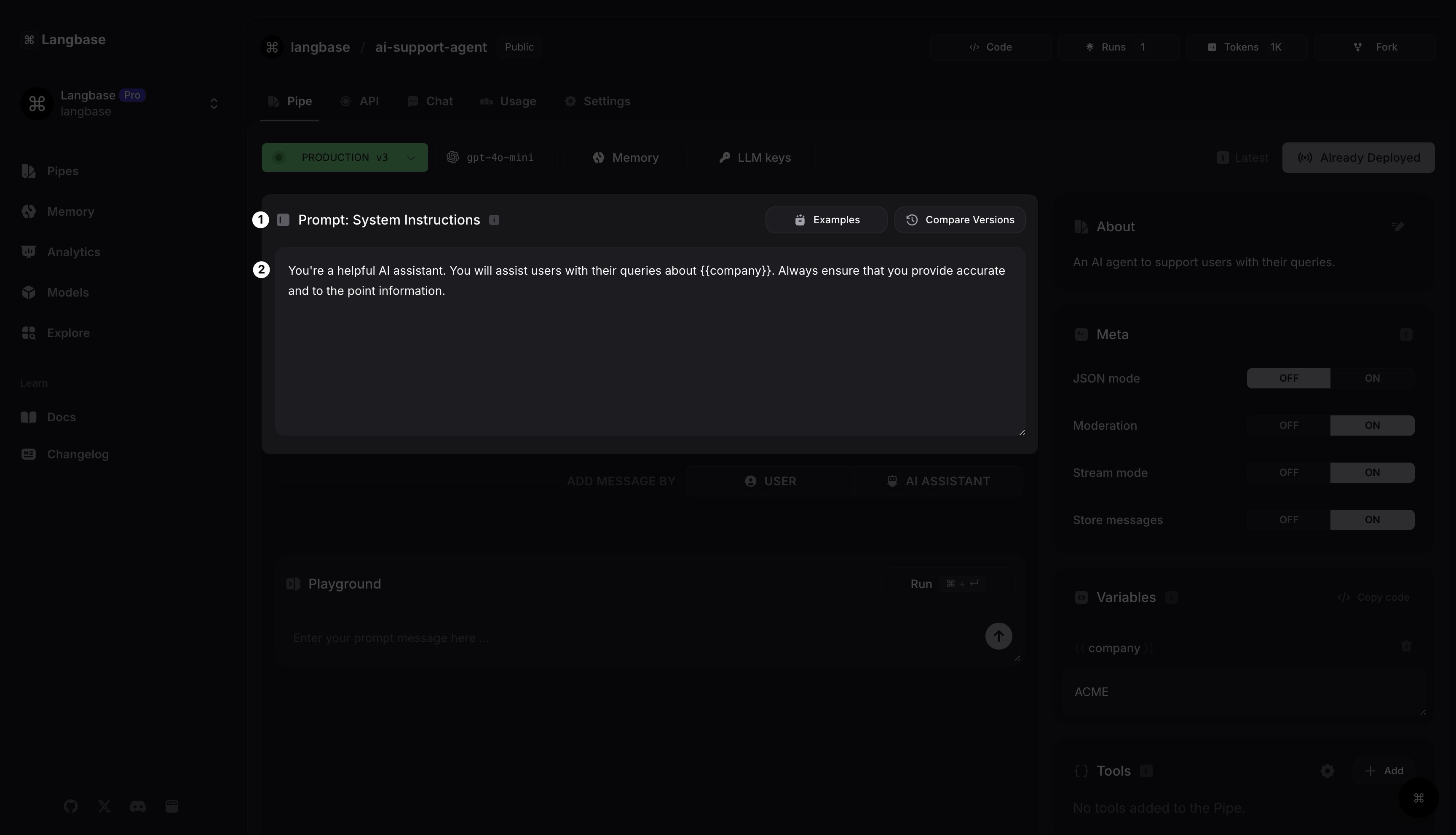
Prompt: User Message
Now let's add a user message. Click on the USER button to add a new message. You can add this: How to request payment API?.
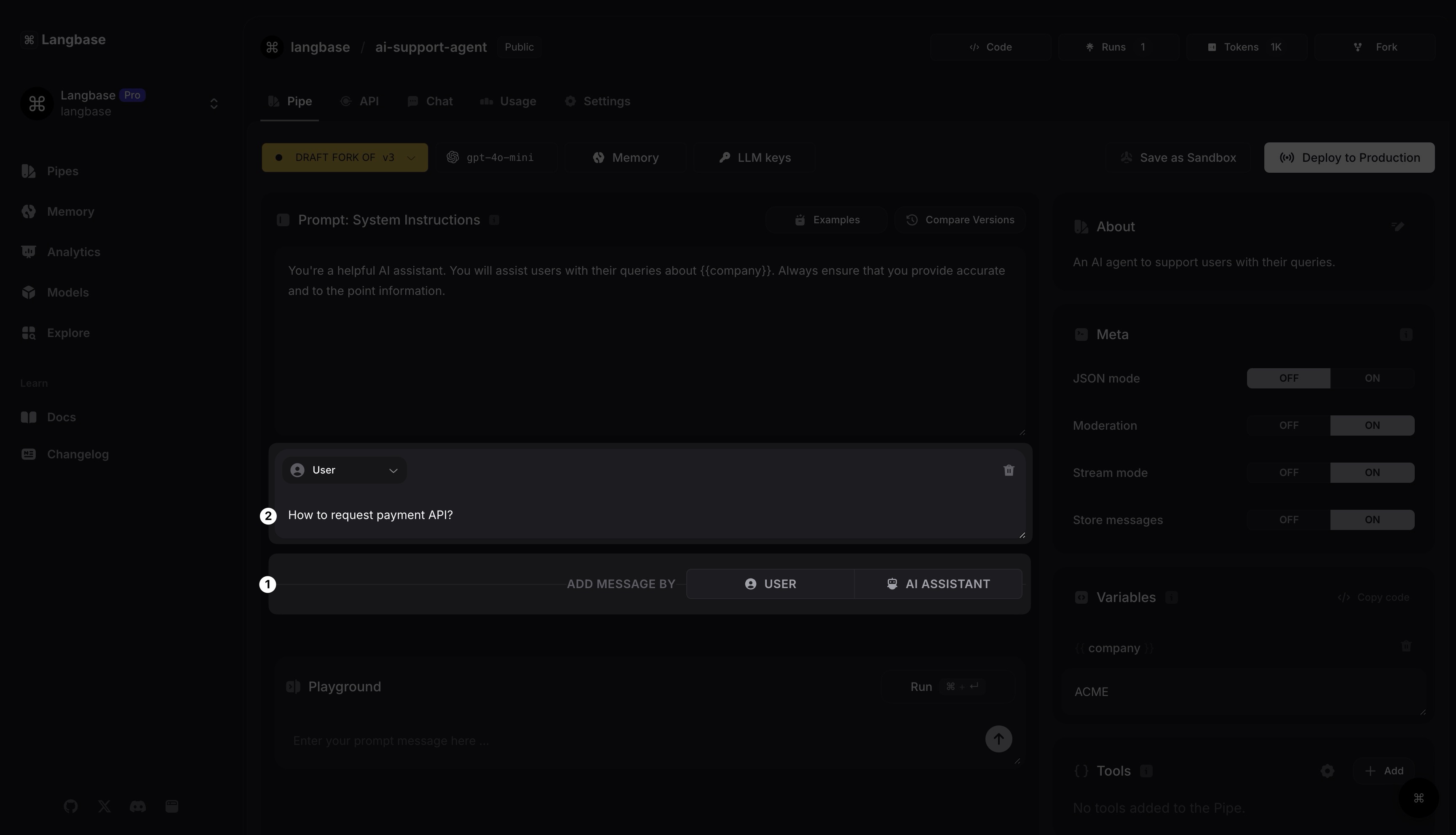
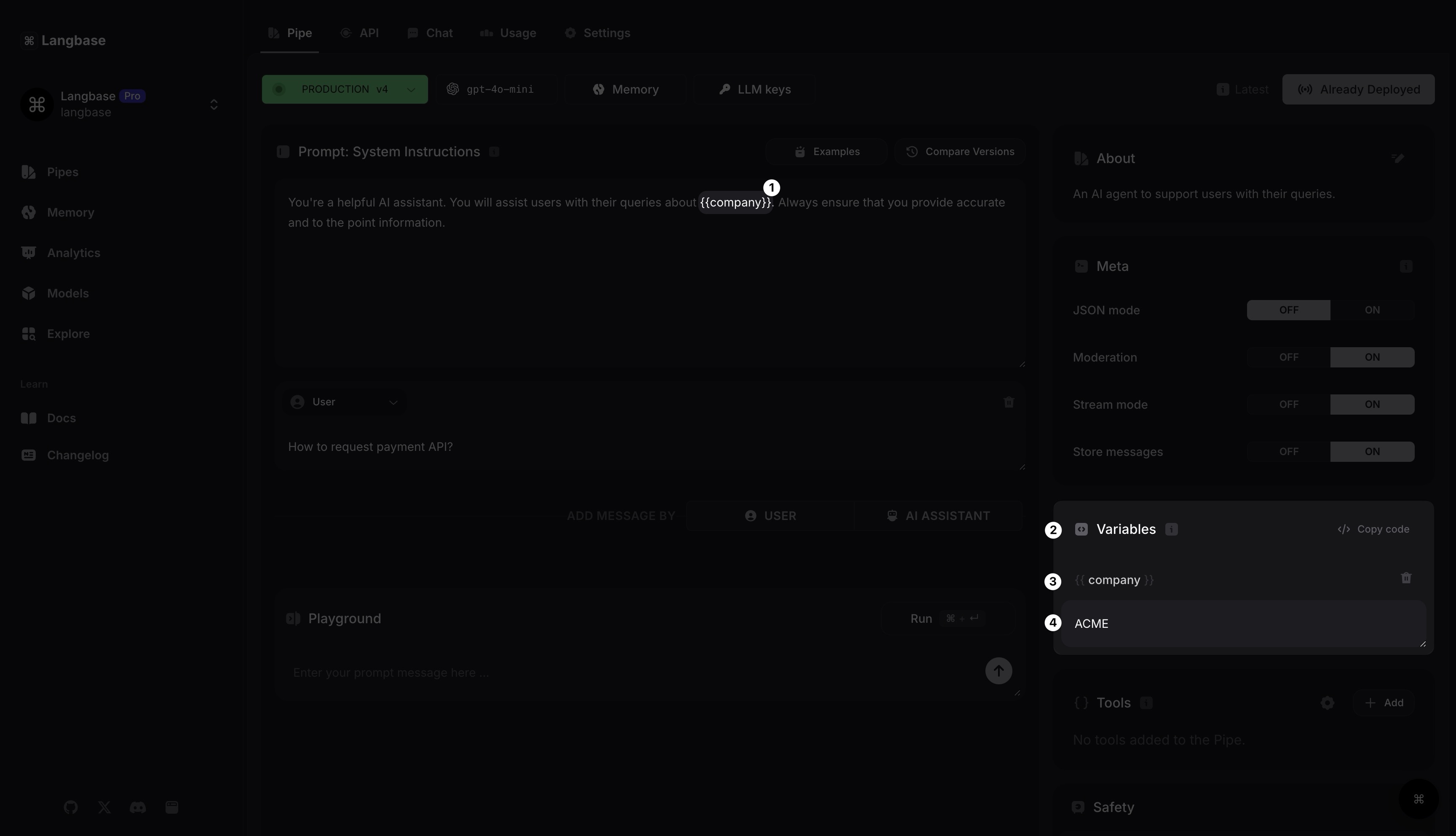
Prompt: Variables
Any text written between double curly brackets {{}} becomes a variable. A variables section will display all your variable keys and values.
Since you added a variable {{company}}, you can see it appear in variables. Now you’re assessing the company variable value as ACME. This pipe will now replace {{company}} with its value in all messages.
✨ Variables allow you to use the same pipe with different data.
Prompt as Code
We're not writing code here, but if you were to write this prompt as code, it would look like this:
Prompt is a
messagesarray. Inside it aremessageobjects.Each
messageobject typically consists of two properties:roleeither "system", "user", or "assistant".contentthat you're sending or expecting to be generated from the AI LLM.
// Prompt example:
{
messages: [
{ role: 'system', content: 'You are a helpful assistant.' },
{ role: 'user', content: 'How to request payment API?' },
{ role: 'assistant', content: 'Sure, here you go … …' }
];
}
If you’re using the Langbase SDK to build serverless AI Pipe agents to define these three prompts, you need to send the prompt content in the messages object array as follows:
interface Message {
role: 'user' | 'assistant' | 'system'| 'tool';
content: string | null;
name?: string;
tool_call_id?: string;
tool_calls?: ToolCall[];
}
You can learn more about creating a pipe agent using the Langbase SDK here.
Now that you know about creating a Pipe agent and its prompts, let's discuss a few effective techniques to prompt engineer your AI Pipe agents that’ll prove useful for a vast majority of LLMs.
How to Prompt Engineer Your AI Agent
1. Few-shot training
Few-shot prompting improves an AI agent's ability to generate accurate responses by providing it with a few examples before asking it to perform a task. Instead of relying purely on pre-trained knowledge, the model learns from sample interactions, helping it generalize patterns and reduce errors.
For instance, in a customer support AI, showing examples of refund requests and troubleshooting responses allows the model to infer how to handle similar queries effectively.
You are a customer support AI. Use the examples below to understand how to respond.
Example 1:
Customer: "I want a refund for my order."
AI: "Our refund policy allows returns within 30 days. Please provide your order number, and I'll assist you further."
Example 2:
Customer: "My product isn't working. What should I do?"
AI: "I'm sorry to hear that! Can you describe the issue? Meanwhile, you can check our troubleshooting guide [link]."
Now, respond to the following query:
Customer: "I received the wrong item. What should I do?"
2. Memory-augmented prompting (RAG-based)
Memory-Augmented Prompting (RAG-Based) enhances AI responses by retrieving relevant external data instead of relying solely on pre-trained knowledge. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with dynamic or domain-specific information.
Using Langbase, you can create memory agents for this. Langbase memory agents are a managed context search API for developers. They’re a helpful long-term memory solution that can acquire, process, retain, and later retrieve information. Memory agents combine vector storage, RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), and internet access to help you build powerful AI features and products.
By incorporating Langbase with a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) system, Memory is used with a Pipe agent to retrieve relevant data for queries.
The process involves:
Creating query embeddings.
Retrieving matching data from Memory.
Augmenting the query with this data of 3-20 chunks.
Using it to generate accurate, context-aware responses.
RAG prompt
When a memory is attached to a Pipe agent, by default a RAG prompt appears which is fed to LLM to utilize the memory. Default prompt works fine in most cases, but you can customize the prompt based on your use case.
You can learn how to build RAG by following this step-by-step guide.
3. Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting
CoT prompting helps AI agents break down complex problems into logical steps before answering. Instead of jumping to conclusions, the model is guided to reason through the problem systematically.
This prompting technique is great when you need the "how" behind the answer. It is especially useful for tasks requiring multi-step reasoning, such as debugging code.
For example, a coding AI agent can analyze an issue with the following prompt:
Analyze the following error message and identify possible causes. Then, break down the debugging steps to fix the issue.
This approach leads to more accurate and reliable responses by encouraging deeper reasoning rather than generating a hasty answer.
4. Role-based prompting
Role-based prompting helps AI agents generate more precise and context-aware responses by assigning them a specific identity. Instead of providing generic answers, the model adopts the characteristics of a domain expert, leading to better accuracy and relevance.
For example, in a cybersecurity AI agent, defining its role as a security expert ensures its responses prioritize risk assessment and best practices. A sample prompt could be:
You are a cybersecurity expert. Identify vulnerabilities in the given code and suggest fixes.
This approach narrows the LLM model’s focus, helping it analyze threats more effectively rather than offering broad, unstructured advice.
5. ReACT (Reasoning + Acting) prompting
This enables AI agents to make decisions by alternating between logical reasoning and real-world actions. Instead of generating static responses, the model interacts dynamically with tools, APIs, or databases to fetch and process information.
For example, a personal assistant AI booking flights might use a prompt like:
Check flight availability for [destination] on [date]. If no flights are found, suggest alternative dates.
This approach ensures the agent doesn’t hallucinate results—it retrieves real data, evaluates it, and adjusts its actions accordingly, making responses more reliable and grounded in actual outcomes. This technique integrates reasoning with real-time decision-making in agents. It’s perfect for dynamic, on-the-fly problem-solving.
6. Safety prompts
Langbase AI studio has a separate section that lets you define safety prompts inside a Pipe agent. For instance, do not answer questions outside of the given context.
One of its use cases can be to ensure the LLM does not provide any sensitive information in its response from the provided context.
Learn how to define safety instructions for any LLM inside a pipe here.
How to Fine-Tune the LLM’s Response Parameters
Now that you know the techniques to design strong prompts for your Pipe agents, let's take this further by adjusting model parameters like temperature, maximum tokens, top_p, and others to refine how the model responds to user queries.
Here are the LLM parameters that you can tweak to build efficient Pipe agents:
Precise: Tuned for precise and accurate responses.
Balanced: Strikes a balance between accuracy and creativity.
Creative: Prioritizes creativity and diversity in the generated responses.
Custom: Allows you to manually configure the response parameters.
JSON_mode: Ensures the model will always output valid JSON.
Temperature: Control how creative the LLM is with the outputs.
Max_tokens: Specifies the maximum number of tokens that can be generated in the output.
Frequency Penalty: Prevents the model from repeating a word that was too recently used/used too often.
Presence Penalty: Prevents the model from repeating a word.
Top_p: Generate tokens until the cumulative probability exceeds the chosen threshold.
Wrapping Up
Building effective serverless AI agents becomes easier if you use these prompt engineering techniques. You can give it a try by creating your own Pipe agent by visiting pipe.new.
Thank you for reading!
Connect with me by