How to install MinIO in Kubernetes in 15 min.
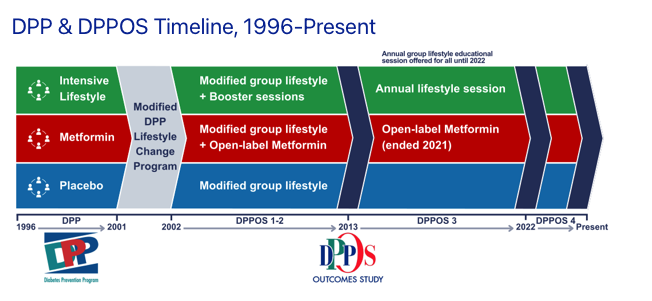
Deploying MinIO on a Kubernetes (K8s) cluster involves installing the MinIO Operator and deploying a MinIO Tenant. The MinIO Operator streamlines the deployment and management of MinIO Tenants, which are isolated MinIO Object Storage instances within your Kubernetes cluster. Install the MinIO Operator The MinIO Operator is a Kubernetes-native application that automates the deployment and management of MinIO Tenants. It extends the Kubernetes API to support MinIO-specific resources, simplifying operations such as provisioning, scaling, and upgrading MinIO clusters. citeturn0search2 To install the MinIO Operator using Kustomize, execute the following command: kubectl apply -k "github.com/minio/operator?ref=v7.0.1" This command fetches the Operator manifests from the specified GitHub repository and applies them to your cluster. The ref=v7.0.1 parameter ensures that version 7.0.1 of the Operator is installed. Create a Namespace for MinIO It's advisable to deploy MinIO Tenants in a dedicated namespace to maintain isolation and manage resources effectively. Create a namespace named minio with the following command: kubectl create namespace minio Deploy a MinIO Tenant A MinIO Tenant represents an independent MinIO Object Storage deployment within your Kubernetes cluster. To deploy a MinIO Tenant, you'll need to create a YAML configuration file (deployment.yaml) that defines the necessary Kubernetes resources. Below is a sample deployment.yaml file. apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: minio --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: storage-configuration namespace: minio stringData: config.env: |- export MINIO_ROOT_USER="minio" export MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD="some-password" export MINIO_STORAGE_CLASS_STANDARD="EC:2" export MINIO_BROWSER="on" export CONSOLE_TLS_ENABLE="on" type: Opaque --- apiVersion: v1 data: CONSOLE_ACCESS_KEY: Y29uc29sZQ== # base64-encoded 'console' CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY: c2Ftb2UtcGFzc3dvcmQ= # base64-encoded 'some-password' kind: Secret metadata: name: storage-user namespace: minio type: Opaque --- apiVersion: minio.min.io/v2 kind: Tenant metadata: name: minio namespace: minio spec: requestAutoCert: true configuration: name: storage-configuration image: quay.io/minio/minio:RELEASE.2024-10-02T17-50-41Z mountPath: /export pools: - name: pool-0 servers: 3 volumesPerServer: 3 volumeClaimTemplate: spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 100Gi storageClassName: local-path users: - name: storage-user Configuration Details The deployment.yaml file comprises several sections: Namespace: Defines the minio namespace for the MinIO Tenant. Secrets: storage-configuration: Contains environment variables for MinIO configuration, such as root user credentials and storage class settings. storage-user: Stores base64-encoded credentials for the MinIO Console access. Tenant Specification: Describes the MinIO Tenant configuration, including: requestAutoCert: Enables automatic TLS certificate generation. image: Specifies the MinIO server image to deploy. mountPath: Sets the directory where storage volumes are mounted. pools: Defines the storage pools, specifying the number of servers, volumes per server, and storage requests. users: Lists the users with access to the MinIO Tenant. Customizable Parameters The following table outlines key parameters in the deployment.yaml file that you may need to adjust based on your environment: Parameter Description Default Value MINIO_ROOT_USER MinIO root username minio MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD MinIO root password some-password CONSOLE_ACCESS_KEY Console access username (base64-encoded) console CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY Console access password (base64-encoded) some-password image MinIO server image version RELEASE.2024-10-02T17-50-41Z servers Number of MinIO server pods 3 volumesPerServer Number of volumes attached to each server 3 storage Storage capacity per volume 100Gi storageClassName Storage class for persistent volumes local-path Ensure that the MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD and CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY values are securely set to strong, unique passwords. The CONSOLE_ACCESS_KEY and CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY values must be base64-encoded. You can encode them using the following command: echo -n 'your-value' | base64 Replace 'your-value' with the actual string you want to encode. Deploy the MinIO Tenant Apply the deployment.yaml configuration to your Kubernetes cluster with the following command: kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml

Deploying MinIO on a Kubernetes (K8s) cluster involves installing the MinIO Operator and deploying a MinIO Tenant. The MinIO Operator streamlines the deployment and management of MinIO Tenants, which are isolated MinIO Object Storage instances within your Kubernetes cluster.
Install the MinIO Operator
The MinIO Operator is a Kubernetes-native application that automates the deployment and management of MinIO Tenants. It extends the Kubernetes API to support MinIO-specific resources, simplifying operations such as provisioning, scaling, and upgrading MinIO clusters. citeturn0search2
To install the MinIO Operator using Kustomize, execute the following command:
kubectl apply -k "github.com/minio/operator?ref=v7.0.1"
This command fetches the Operator manifests from the specified GitHub repository and applies them to your cluster. The ref=v7.0.1 parameter ensures that version 7.0.1 of the Operator is installed.
Create a Namespace for MinIO
It's advisable to deploy MinIO Tenants in a dedicated namespace to maintain isolation and manage resources effectively. Create a namespace named minio with the following command:
kubectl create namespace minio
Deploy a MinIO Tenant
A MinIO Tenant represents an independent MinIO Object Storage deployment within your Kubernetes cluster. To deploy a MinIO Tenant, you'll need to create a YAML configuration file (deployment.yaml) that defines the necessary Kubernetes resources. Below is a sample deployment.yaml file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: minio
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: storage-configuration
namespace: minio
stringData:
config.env: |-
export MINIO_ROOT_USER="minio"
export MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD="some-password"
export MINIO_STORAGE_CLASS_STANDARD="EC:2"
export MINIO_BROWSER="on"
export CONSOLE_TLS_ENABLE="on"
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
CONSOLE_ACCESS_KEY: Y29uc29sZQ== # base64-encoded 'console'
CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY: c2Ftb2UtcGFzc3dvcmQ= # base64-encoded 'some-password'
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: storage-user
namespace: minio
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: minio.min.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: minio
namespace: minio
spec:
requestAutoCert: true
configuration:
name: storage-configuration
image: quay.io/minio/minio:RELEASE.2024-10-02T17-50-41Z
mountPath: /export
pools:
- name: pool-0
servers: 3
volumesPerServer: 3
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Gi
storageClassName: local-path
users:
- name: storage-user
Configuration Details
The deployment.yaml file comprises several sections:
Namespace: Defines the
minionamespace for the MinIO Tenant.-
Secrets:
-
storage-configuration: Contains environment variables for MinIO configuration, such as root user credentials and storage class settings. -
storage-user: Stores base64-encoded credentials for the MinIO Console access.
-
-
Tenant Specification: Describes the MinIO Tenant configuration, including:
-
requestAutoCert: Enables automatic TLS certificate generation. -
image: Specifies the MinIO server image to deploy. -
mountPath: Sets the directory where storage volumes are mounted. -
pools: Defines the storage pools, specifying the number of servers, volumes per server, and storage requests. -
users: Lists the users with access to the MinIO Tenant.
-
Customizable Parameters
The following table outlines key parameters in the deployment.yaml file that you may need to adjust based on your environment:
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
MINIO_ROOT_USER |
MinIO root username | minio |
MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD |
MinIO root password | some-password |
CONSOLE_ACCESS_KEY |
Console access username (base64-encoded) | console |
CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY |
Console access password (base64-encoded) | some-password |
image |
MinIO server image version | RELEASE.2024-10-02T17-50-41Z |
servers |
Number of MinIO server pods | 3 |
volumesPerServer |
Number of volumes attached to each server | 3 |
storage |
Storage capacity per volume | 100Gi |
storageClassName |
Storage class for persistent volumes | local-path |
Ensure that the MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD and CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY values are securely set to strong, unique passwords. The CONSOLE_ACCESS_KEY and CONSOLE_SECRET_KEY values must be base64-encoded. You can encode them using the following command:
echo -n 'your-value' | base64
Replace 'your-value' with the actual string you want to encode.
Deploy the MinIO Tenant
Apply the deployment.yaml configuration to your Kubernetes cluster with the following command:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml











![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)
























/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/76/04/7604f174-2171-4526-ab80-663c49cb0c84/coffee_opener.jpg?#)