Distant star explosions could have wiped out life on Earth twice
A team of scientists says two mass extinctions linked to ice ages could have been caused by supernovas many light-years away from Earth.


Most people know the theory that an asteroid smashed into Earth — hitting what is now the Yucatán Peninsula — and killed off many of the dinosaurs about 66 million years ago.
But that was not the only mass extinction for the planet — just the most well-known. Scientists believe at least five mass extinctions have occurred in the past 500 million years, and not all of them were caused by menacing space rocks. Perhaps two of them, one 372 million years ago and another 445 million years ago, were ice ages.
A new study, based on a census of stars in the Milky Way, suggests those periods of severely cold climates may have begun with stars dying light-years away.
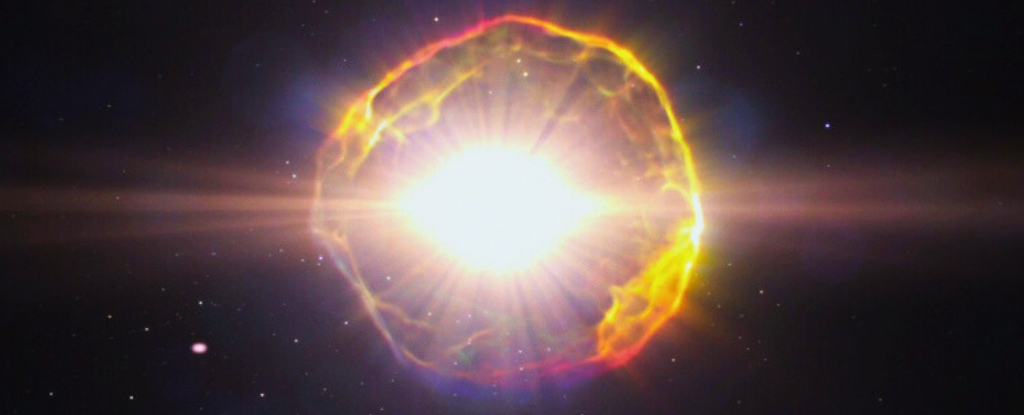
"If a massive star were to explode as a supernova close to the Earth, the results would be devastating for life on Earth," said Nick Wright, an astrophysicist at Keele University in the United Kingdom, in a statement. "This research suggests that this may have already happened."

Previous research has yet to determine the cause for either the late Devonian or Ordovician mass extinctions, which occurred 372 and 445 million years ago, respectively. The Ordovician extinction is thought to have killed off about 60 percent of the invertebrate sea creatures at a time when most of Earth's species lived in the ocean; the late Devonian event eliminated 70 percent of all creatures and influenced sweeping changes in the kinds of fish that survived.
Scientists have suspected these ice ages followed damage to the ozone layer. Crucially, the team working on the census says supernovas could have triggered the catastrophic changes in Earth's protective atmosphere. The rate of supernovas near Earth is consistent with the timing of both mass extinctions. The team's findings appear in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
A supernova is a cataclysmic stellar death that leaves behind a black hole or neutron star. It is the biggest, brightest, and most violent type of explosion scientists have observed in the universe.
These cosmic blasts are element factories, NASA says: They create carbon, for instance, the same chemical on which humans and much of life on Earth are based. They spread calcium and iron, the same stuff found in bones and blood, across interstellar space. This dispersal seeds new generations of stars and planets.
This is what astronomer Carl Sagan meant when he said we're made of "star stuff." The same substances composing our bodies were literally forged within the cores of stars, then flung through the cosmos when they died.
It's a great paradox then that supernovas could be both creators and destroyers of life, the authors observed.
"Supernova explosions bring heavy chemical elements into the interstellar medium, which are then used to form new stars and planets," said Alexis Quintana, lead author, in a statement. "But if a planet, including the Earth, is located too close to this kind of event, this can have devastating effects."
A nearby supernova's blast of various forms of radiation could strip away the ozone layer. By "near," the experts mean within 65 light-years or so. Without the ozone, Earth would be exposed to harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun and acid rain.

Using models that estimate how stars evolve and emit light at different wavelengths, the team analyzed data from large sky surveys, including data from the European Space Agency's recently retired Gaia mission. The census involved nearly 25,000 so-called "OB stars" — very hot, massive stars — within 1,000 parsecs, or roughly 3,260 light-years, of the sun. These stars are so hot, they're at least double the sun's surface temperature.
This census allowed the scientists to calculate the rate of supernovas in the local region of the galaxy and throughout the Milky Way as a whole. According to the team's calculations, about one supernova happens every 400 million years within close enough vicinity to Earth that its radiation could impact the atmosphere.
The nearest stars that could blow within the next million years are thought to be Antares and Betelgeuse. If that gives you chills, don't worry: Both stars are more than 500 light-years away — far enough that their blasts wouldn't likely trigger an ice age.
















_Yuri_Arcurs_Alamy.jpg?#)



















![Watch a SpaceX rocket launch Crew-10 relief mission March 14 for NASA astronauts on ISS after delay [updated]](https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/TBuLj3rJngaWrbyogNud9H.jpg?#)









































