Java Comparable
Comparable: It is used to define the natural ordering of the objects within the class.--->method..compareTo() Comparator:(TBD) It is used to define custom sorting logic externally.method..compare() package collections; public class mobile implements Comparable { String brand; int price; int ram; double weigth; mobile(String brand, int price, int ram, double weigth) { this.brand = brand; this.price = price; this.ram = ram; this.weigth = weigth; } public String toString() { return this.brand + " " + this.price + " " + this.ram + " " + this.weigth; } public int compareTo(Object o) // call compareTo as m1 and passes parameters as m2 { // System.out.println("First "+ this.price);//m1(print and see how compare happen) mobile m = (mobile) o;// converting mobile class object // System.out.println("second "+ m.price);//m2(print and see how compare happen) if (this.price > m.price) { return 1;// ascending } else if (this.price < m.price) { return -1;// decending } return 0;//equal } } package collections; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Iterator; public class mobshop { public static void main(String[] args) { mobile m1 = new mobile("samsang", 15000, 12, 5.0); mobile m2 = new mobile("vivo", 10000, 6, 7.0); mobile m3 = new mobile("apple", 100000, 4, 5.0); ArrayList al = new ArrayList(); al.add(m1); al.add(m2); al.add(m3); System.out.println("Before Sorting: " + al); Collections.sort(al);// use to sort in order System.out.println("After Sorting: " + al); int max_price = 0; String brand = " "; Iterator it = al.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { mobile mob = (mobile) it.next(); if (mob.price > max_price) { max_price = mob.price; brand = mob.brand; } } System.out.println(max_price + " brand = " + brand); } } Output: Before Sorting: [samsang 15000 12 5.0, vivo 10000 6 7.0, apple 100000 4 5.0] After Sorting: [vivo 10000 6 7.0, samsang 15000 12 5.0, apple 100000 4 5.0] 100000 brand = apple Reference:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/comparable-vs-comparator-in-java/
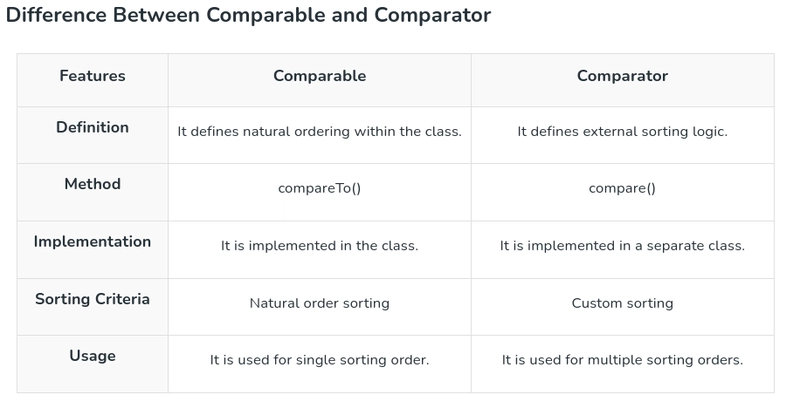
Comparable: It is used to define the natural ordering of the objects within the class.--->method..compareTo()
Comparator:(TBD) It is used to define custom sorting logic externally.method..compare()
package collections;
public class mobile implements Comparablepackage collections;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class mobshop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
mobile m1 = new mobile("samsang", 15000, 12, 5.0);
mobile m2 = new mobile("vivo", 10000, 6, 7.0);
mobile m3 = new mobile("apple", 100000, 4, 5.0);
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(m1);
al.add(m2);
al.add(m3);
System.out.println("Before Sorting: " + al);
Collections.sort(al);// use to sort in order
System.out.println("After Sorting: " + al);
int max_price = 0;
String brand = " ";
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
mobile mob = (mobile) it.next();
if (mob.price > max_price) {
max_price = mob.price;
brand = mob.brand;
}
}
System.out.println(max_price + " brand = " + brand);
}
}
Output:
Before Sorting: [samsang 15000 12 5.0, vivo 10000 6 7.0, apple 100000 4 5.0]
After Sorting: [vivo 10000 6 7.0, samsang 15000 12 5.0, apple 100000 4 5.0]
100000 brand = apple
Reference:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/comparable-vs-comparator-in-java/









































































