I’m a Clinical Weight-Loss Practitioner. These Are the Best Weight-Loss Diets That Actually Work
Clinically proven ways to shed weight and keep it off.
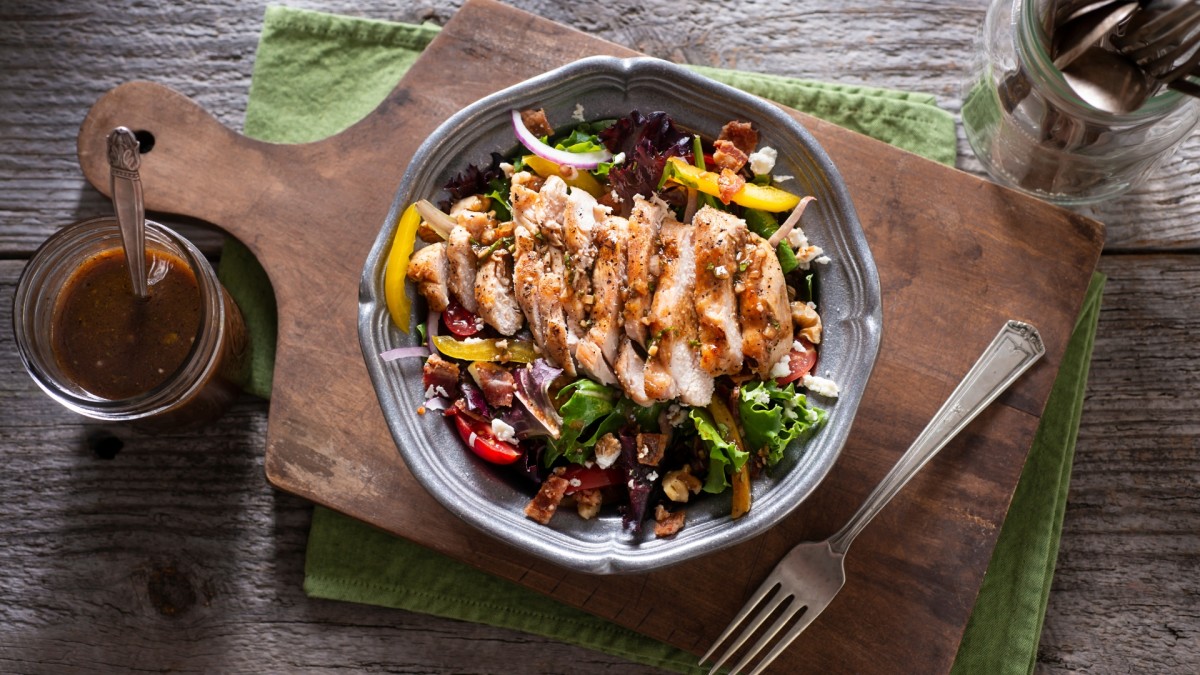

When it comes to weight loss, there’s no magic bullet that works for everyone. As a certified nutrition coach and clinical weight-loss practitioner, I believe the best diets for weight loss are those that individuals can maintain long-term. This sustainable approach helps foster a positive relationship with food and allows for the development of healthy habits that not only lead to weight loss, but also make it possible to keep the weight off over time.
While various weight-loss diets differ in food choices, meal timing, and macronutrient recommendations, they all share one fundamental principle: They help individuals achieve a calorie deficit, which is essential for weight loss.
In this article, we’ll explore eight of the best diets for weight loss that follow sound nutritional principles without resorting to extreme calorie restriction or unsustainable macronutrient imbalances. This means we’re steering clear of any fad diets that promise quick fixes but rarely deliver lasting results. I know it sounds cliche, but when it comes to weight loss, slow and steady really does win the race.
Best Diets for Weight Loss
All of the diets on this list share key principles: they emphasize whole, unprocessed foods, encourage cooking at home, and promote moderation in regard to sugar and alcohol. Keep in mind that you don’t need to follow a specific diet to lose weight—what matters most is finding a sustainable approach that fits your lifestyle.
1. Mediterranean Diet

Getty Images/SimpleImages
The Mediterranean diet is inspired by the traditional eating habits of individuals living in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. Primarily plant-based, the diet emphasizes the consumption of vegetables, legumes, whole grains, fruits, and olive oil, with the occasional inclusion of seafood, poultry, and dairy. Some common staples in the Mediterranean diet include olive oil, leafy greens, potatoes, chickpeas, feta cheese, lemon, and honey.
This diet is a popular choice for weight loss because of its focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that promote satiety and provide essential nutrients without an excess of calories. Its balanced approach, centered around healthy fats, lean proteins, and fiber-rich produce, can help regulate hunger and maintain long-term weight management.
2. Okinawan Diet

Getty Images/Elena_Danileiko
The Okinawan diet is based on the traditional dietary patterns of people living on Okinawa, a Japanese island known for its high life expectancy and low rates of chronic disease. This diet is plant-based, focusing on vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and fruits, with moderate amounts of fish and small portions of lean meat. Key staples of the Okinawan diet include sweet potatoes, tofu, brown rice, seaweed, miso, fish, and green tea, the latter of which is rich in antioxidants.
The Okinawan diet supports weight loss by emphasizing nutrient-dense, high-fiber foods that promote satiety and help regulate appetite. Its foundation in whole, unprocessed ingredients naturally leads to a lower calorie intake without sacrificing essential nutrients. Another key aspect of this diet is the cultural practice of hara hachi bu, which encourages eating until you’re about 80 percent full. This helps foster mindful eating habits and prevents overeating.
3. Paleo Diet

Getty Images/Claudia Totir
The paleo diet is centered around the principle of eating whole, unprocessed foods that our ancestors would have consumed during the Paleolithic era. This includes lean meats, fish, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and healthy fats while avoiding grains, legumes, dairy, refined sugars, and processed foods.
The idea behind the diet is that modern processed foods contribute to many health issues, including obesity, inflammation, and metabolic disorders, and that returning to a more natural way of eating can promote better overall health. One of the primary reasons the paleo diet may aid in weight loss is its focus on high-protein, high-fiber foods that promote satiety and reduce cravings.
Protein is essential for muscle maintenance and plays a key role in boosting metabolism, while fiber from fruits and vegetables helps regulate digestion and prevent overeating. Additionally, by cutting out refined carbohydrates and processed sugars, the paleo diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing energy crashes and cravings that may lead to overeating. Since the diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, many individuals naturally consume fewer calories without the need for strict portion control or calorie counting, making it a sustainable approach to long-term weight management.
4. DASH Diet

Getty Images/pjohnson1
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet was originally developed to help lower blood pressure, but it's also been shown to support weight loss and improve overall health. This diet emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while limiting sodium, added sugars, and saturated fats. By focusing on fiber-rich and protein-packed foods, the DASH diet helps promote satiety, making it easier to maintain a calorie deficit without feeling deprived.
The ENCORE study looked at the combination of the DASH diet with exercise to support weight loss and improve cardiovascular biomarkers in both men and women. This research highlighted how incorporating consistent physical activity alongside a balanced, nutrient-rich diet like DASH can significantly enhance weight loss outcomes. Regular exercise not only helps burn calories, but also boosts metabolism, strengthens the heart, and improves overall cardiovascular health, making it a crucial component of any effective weight-loss strategy.
Related: The Sleep Hack That Supercharges Muscle Repair While You Rest
5. Flexitarian Diet

Getty Images/Kseniya Ovchinnikova
The flexitarian diet is a plant-forward approach that allows for occasional meat consumption, offering the health benefits of a predominantly plant-based diet without the strict restrictions of vegetarianism or veganism. This diet emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and plant-based proteins, while limiting processed foods and refined sugars. The Flexitarian diet provides a flexible, sustainable approach to healthy eating by striking a balance between plant-based eating and moderate meat consumption.
Research supports the benefits of this approach—a review published in Frontiers in Nutrition found that flexitarian diets may contribute to maintaining a healthy body weight, improving metabolism, regulating blood pressure, and lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes.
6. Plant-Based Diet

Getty Images/Yagi Studio
Plant-based diets can be highly effective for weight loss due to their emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods that are typically lower in calories and high in fiber. Whether you're consuming mostly plant-based foods or following a more restrictive approach like vegetarianism or veganism, the focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds provides a wealth of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants while keeping your total calories in check.
There are various levels to adopting a plant-based approach, from incorporating more plant-based meals into your diet to fully committing to vegetarianism or veganism. Vegetarianism eliminates meat and fish, but still includes dairy and eggs, while veganism eliminates all animal products, focusing entirely on plant-based foods. Each level of commitment can offer unique benefits for weight loss, but all of them encourage healthier eating habits that can help manage weight in the long term.
7. Pescatarian Diet

Getty Images/Rawpixel
The pescatarian diet is a plant-based eating plan that includes fish and other seafood as the primary protein source while eliminating animal meat and poultry. This diet is often considered a healthier alternative to traditional omnivorous diets because it prioritizes nutrient-dense, whole foods like vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, and healthy fats.
Fish, particularly fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, provides high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential nutrients that support heart health. By focusing on seafood, the pescatarian diet reduces the intake of red meat, which is higher in saturated fat and calories, making it easier to maintain a calorie deficit—a key component of weight loss. The inclusion of protein-rich foods like fish also helps promote feelings of fullness, making it easier to control portion sizes and avoid overeating. It's also more flexible than fully plant-based diets, making it easier for those who are not ready to completely eliminate animal products to transition to a healthier, lower-calorie diet that still provides essential nutrients.
8. Intermittent Fasting

Getty Images/Lordn
Intermittent fasting focuses not on what you eat, but when you eat. The most common method, known as the 16/8 approach, involves fasting for 16 hours and consuming all daily calories within an eight-hour eating window. The idea behind this is that limiting the timeframe for eating makes it more difficult to overeat, as opposed to a traditional unrestricted diet. However, if weight loss is your primary goal, it’s important to still pay attention to the types of foods you eat during your eating window, as calorie-dense or unhealthy options can undermine your progress.
A comprehensive review of 40 studies published in Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology found that intermittent fasting can be an effective strategy for weight loss. Participants who followed intermittent fasting lost as much as 11 pounds over the course of 10 weeks, demonstrating its potential for helping individuals shed excess weight.
Related: I'm a Registered Dietitian. Here's How to Lose 5 Pounds Safely
How to Choose the Best Diet for You
Choosing the best diet for you starts with understanding your individual needs, preferences, and goals. The diet you choose should fit seamlessly into your daily life, so consider factors like your schedule, cooking habits, and personal food preferences. It’s also essential that your diet meets your nutritional needs. If you have dietary restrictions like a gluten or dairy intolerance, prefer a plant-based lifestyle, or simply dislike certain foods, then look for a diet that can accommodate those needs.
How to Structure a Diet for Weight Loss
If your primary goal is weight loss, the key is to create a sustainable calorie deficit. Rather than drastically cutting your daily caloric intake right away, aim for a moderate reduction of 200 to 300 calories per day. This gradual approach helps ensure long-term success and prevents your metabolism from slowing down too much.
It's important to remember that weight loss is a dynamic process, and as you lose weight, your caloric needs will decrease. This is why large calorie reductions, like 500 to 1,000 calories per day, may not be sustainable in the long run. For reference, the National Institute of Health’s clinical guidelines on obesity describe a safe rate of weight loss as 0.5 to one kilogram per week.
Here are some practical tips to help you structure a weight-loss diet.
- Start with a modest caloric reduction of 200 to 300 calories per day.
- Once you plateau for about a week, reduce your intake slightly to continue progress. Adjust as needed.
- Prioritize whole foods—focusing on nutrient-dense, minimally processed foods that nourish your body.
- Include protein at every meal—protein supports muscle mass and keeps you feeling full.
- Limit processed foods, added sugars, fried foods, and alcohol. These can contribute to unnecessary calories and hinder progress.
Related: How to Lose 1 Pound a Week: A Sustainable Guide to Lose Weight and Keep It Off
What Is the Best Way to Lose Weight?
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to weight loss. What works for one person may not work for another. However, one fundamental principle remains the same: Weight loss is only possible by creating a negative energy balance. In other words, you must burn more calories than you consume.
Fortunately, there are multiple ways to achieve a calorie deficit. You can reduce your calorie intake, increase physical activity, or utilize a combination of the two. The key to long-term success is finding an approach that is safe, sustainable, and fits your lifestyle.
If you're looking for actionable advice, I highly recommend using a nutrition tracking app to help you understand where your daily calories come from and keep you accountable to your weight loss goals. Even tracking for just a few days can reveal hidden sources of excess calories and help you make more informed dietary choices.
For example, you might realize that your morning latte contains far more calories than expected. Simply switching to a black coffee could save you hundreds of calories per day. Other common sources of sneaky calories include calorie-dense foods like cooking oils and peanut butter, condiments like ketchup and barbecue sauce, salad dressings, and sugary drinks such as soda, lemonade, or sweet tea. Small adjustments in these areas can make a big difference over time, jump-starting your weight loss journey without drastically changing your current routine.