From JavaScript to VBA: Navigating Variable Declaration and Management
Transitioning from JavaScript to VBA? This article covers the key aspects of variable declaration and management in VBA. Embrace this structured approach to ensure a smooth transition from JavaScript! Article Concept Overview Problem: Transitioning from JavaScript to VBA can be daunting due to differences in variable declaration and management. JavaScript's dynamic typing and modern code editors provide a flexible environment, whereas VBA requires a more structured approach to variable declaration and debugging. This can lead to confusion and inefficiencies, especially for those accustomed to JavaScript's flexible nature and advanced debugging tools. Solution: This article aims to bridge the gap between JavaScript and VBA by focusing on the essential aspect of variable declaration. You can effectively manage variables by understanding the syntax and structure of VBA, including using the Dim keyword and various data types. What is Microsoft VBA and Why You Should Learn It VBA, or Visual Basic for Applications, is a programming language developed by Microsoft to automate tasks and enhance functionality in Office applications like Excel, Word, and Access. It allows you to create macros for repetitive tasks, manage data, and perform complex calculations. Integrated into Office, VBA offers a user-friendly environment for beginners and experienced programmers to improve tool capabilities and streamline workflows. Learning VBA is particularly beneficial in corporate settings where Microsoft Office is widely used. Mastering VBA enhances Excel's functionalities, making you a valuable asset by creating custom programs that save both time and money. These programs can range from basic data entry automation to complex integrations across Office applications. For more detailed insights, refer to my first article in this series. Enabling the Developer Tab in Excel for VBA Access To begin using VBA in Excel, you must enable the "Developer" tab, which provides access to the VBA editor and various tools for managing macros. For detailed guidance on how to set up the "Developer" tab, please refer to my article "Getting Started with VBA in Excel." In that article, I explain the step-by-step process of enabling the "Developer" tab, accessing the VBA editor, and preparing your Excel environment for VBA use. Understanding Variables in JavaScript JavaScript's dynamic typing offers flexibility but can cause runtime errors if types aren't managed well. This is useful for quick development but needs careful handling to prevent issues. Unlike JavaScript, VBA requires explicit declaration and typing, reducing type-related errors and promoting disciplined variable management. Understanding this difference is crucial for those transitioning from JavaScript to VBA. Comparison with JavaScript: JavaScript uses var, let, and const to declare variables, and it is dynamically typed, meaning you don't specify the data type. Variables can hold any type of data and can change types during execution. let and const provide block scope, while var provides function scope. This differs from VBA's more rigid scope rules. Example in JavaScript: let age = 25; declares a variable age that can hold any type of data, initially a number. JavaScript's flexibility allows age to later hold a string, like age = "twenty-five";, which is not possible in VBA without changing the variable's declaration. Understanding Variables in VBA In VBA, a variable is a named storage spot for data that can change during a program. Variables store, retrieve, and manipulate data. They must be declared with a data type using the Dim keyword, which helps use memory efficiently and reduces errors. Explicit typing ensures consistent use and optimizes memory by allocating the right space for each variable. Declaration: In VBA, you use Dim to declare a variable, specifying its name and data type. For example: Dim age As Integer. This declaration allocates memory for the variable and defines the type of data it can hold, ensuring efficient memory usage and reducing errors. Explicit Typing: VBA requires explicit typing, meaning you must specify the data type of each variable. This helps prevent type-related errors and ensures consistent use of variables. Example: Dim name As String declares a variable name that can only hold text. Scope: The scope of a variable declared with Dim depends on where it is declared. If declared within a procedure, it is local to that procedure. If declared at the module level, it is accessible throughout the module. Understanding Dim and its role in VBA is crucial for writing structured and error-free code. It enforces a disciplined approach to variable management, contrasting with JavaScript's more flexible but potentially error-prone dynamic typing. VBA Data Types Understanding the various data types available
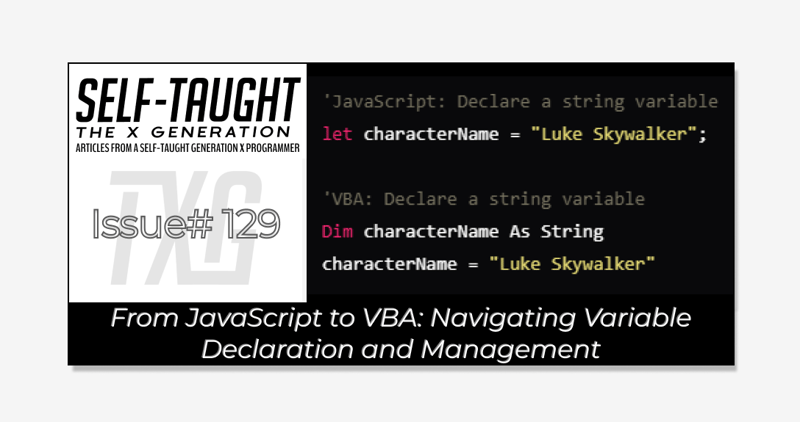
Transitioning from JavaScript to VBA? This article covers the key aspects of variable declaration and management in VBA. Embrace this structured approach to ensure a smooth transition from JavaScript!
Article Concept Overview
Problem:
Transitioning from JavaScript to VBA can be daunting due to differences in variable declaration and management. JavaScript's dynamic typing and modern code editors provide a flexible environment, whereas VBA requires a more structured approach to variable declaration and debugging. This can lead to confusion and inefficiencies, especially for those accustomed to JavaScript's flexible nature and advanced debugging tools.
Solution:
This article aims to bridge the gap between JavaScript and VBA by focusing on the essential aspect of variable declaration. You can effectively manage variables by understanding the syntax and structure of VBA, including using the Dim keyword and various data types.
What is Microsoft VBA and Why You Should Learn It
VBA, or Visual Basic for Applications, is a programming language developed by Microsoft to automate tasks and enhance functionality in Office applications like Excel, Word, and Access. It allows you to create macros for repetitive tasks, manage data, and perform complex calculations. Integrated into Office, VBA offers a user-friendly environment for beginners and experienced programmers to improve tool capabilities and streamline workflows.
Learning VBA is particularly beneficial in corporate settings where Microsoft Office is widely used. Mastering VBA enhances Excel's functionalities, making you a valuable asset by creating custom programs that save both time and money. These programs can range from basic data entry automation to complex integrations across Office applications. For more detailed insights, refer to my first article in this series.
Enabling the Developer Tab in Excel for VBA Access
To begin using VBA in Excel, you must enable the "Developer" tab, which provides access to the VBA editor and various tools for managing macros. For detailed guidance on how to set up the "Developer" tab, please refer to my article "Getting Started with VBA in Excel." In that article, I explain the step-by-step process of enabling the "Developer" tab, accessing the VBA editor, and preparing your Excel environment for VBA use.
Understanding Variables in JavaScript
JavaScript's dynamic typing offers flexibility but can cause runtime errors if types aren't managed well. This is useful for quick development but needs careful handling to prevent issues. Unlike JavaScript, VBA requires explicit declaration and typing, reducing type-related errors and promoting disciplined variable management. Understanding this difference is crucial for those transitioning from JavaScript to VBA.
Comparison with JavaScript:
JavaScript uses
var,let, andconstto declare variables, and it is dynamically typed, meaning you don't specify the data type. Variables can hold any type of data and can change types during execution.letandconstprovide block scope, whilevarprovides function scope. This differs from VBA's more rigid scope rules.
Example in JavaScript:
let age = 25;declares a variableagethat can hold any type of data, initially a number.JavaScript's flexibility allows
ageto later hold a string, likeage = "twenty-five";, which is not possible in VBA without changing the variable's declaration.
Understanding Variables in VBA
In VBA, a variable is a named storage spot for data that can change during a program. Variables store, retrieve, and manipulate data. They must be declared with a data type using the Dim keyword, which helps use memory efficiently and reduces errors. Explicit typing ensures consistent use and optimizes memory by allocating the right space for each variable.
Declaration:
In VBA, you use
Dimto declare a variable, specifying its name and data type. For example:Dim age As Integer.This declaration allocates memory for the variable and defines the type of data it can hold, ensuring efficient memory usage and reducing errors.
Explicit Typing:
VBA requires explicit typing, meaning you must specify the data type of each variable. This helps prevent type-related errors and ensures consistent use of variables.
Example:
Dim name As Stringdeclares a variablenamethat can only hold text.
Scope:
- The scope of a variable declared with
Dimdepends on where it is declared. If declared within a procedure, it is local to that procedure. If declared at the module level, it is accessible throughout the module.
Understanding Dim and its role in VBA is crucial for writing structured and error-free code. It enforces a disciplined approach to variable management, contrasting with JavaScript's more flexible but potentially error-prone dynamic typing.
VBA Data Types
Understanding the various data types available in VBA is crucial for efficient programming and memory management. Each data type serves a specific purpose, allowing you to store and manipulate data effectively. By choosing the appropriate data type for your variables, you can optimize performance and reduce errors in your VBA projects.
Below is a comprehensive list of data types you can utilize in VBA to handle different kinds of data and calculations.
Byte: Stores integer values from 0 to 255.
Integer: Stores whole numbers from -32,768 to 32,767.
Long: Stores larger whole numbers from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
LongLong: Available in 64-bit versions of VBA, stores even larger whole numbers.
LongPtr: Used for pointers and handles, size depends on the platform (32-bit or 64-bit).
Single: Single-precision floating-point for numbers with decimals.
Double: Double-precision floating-point for more precise decimal calculations.
Currency: Fixed-point for financial calculations, supporting four decimal places.
Decimal: High-precision calculations, used as a subtype of Variant.
String: Stores sequences of characters (text).
Boolean: Represents logical values,
TrueorFalse.Date: Stores date and time values.
Variant: Can hold any type of data, including numbers, strings, and objects.
Object: Stores references to objects for manipulation within VBA.
These data types provide a range of options for handling different kinds of data and calculations in VBA, allowing for efficient and precise programming.
Exploring VBA Data Types Through a Star Wars Character Example
This VBA program provides a practical demonstration of how various data types can be utilized to represent and manage information about a Star Wars character!
By declaring variables with specific data types, such as Byte, Integer, Long, and others, the program efficiently stores and manipulates character attributes like rank, age, and force power level. This example not only highlights the versatility of VBA's data types but also offers a fun and engaging way to understand their application in real-world scenarios.
Sub StarWarsCharacterInfo()
' Declare variables using different data types
Dim characterRank As Byte
Dim characterAge As Integer
Dim characterID As Long
Dim midichlorianCount As LongLong
Dim pointerExample As LongPtr ' Used for demonstration, not functional in this context
Dim characterHeight As Single
Dim forcePowerLevel As Double
Dim credits As Currency
Dim preciseCalculation As Variant ' Decimal is used as a subtype of Variant
Dim characterName As String
Dim isJedi As Boolean
Dim birthDate As Date
Dim characterDescription As Variant
Dim characterObject As Object ' Example object, not functional in this context
' Assign values to the variables
characterRank = 5
characterAge = 19
characterID = 1001
midichlorianCount = 20000
' pointerExample is not assigned as it's for demonstration
characterHeight = 1.72
forcePowerLevel = 9000.5
credits = 1500.75
preciseCalculation = CDec(12345.6789) ' Example Decimal value using CDec
characterName = "Luke Skywalker"
isJedi = True
birthDate = #7/24/1976# ' fictional date
characterDescription = "A young farm boy who becomes a Jedi Knight."
' characterObject is not assigned as it's for demonstration
' Display the character information
MsgBox "Character Rank: " & characterRank & vbCrLf & _
"Age: " & characterAge & vbCrLf & _
"Character ID: " & characterID & vbCrLf & _
"Midichlorian Count: " & midichlorianCount & vbCrLf & _
"Height: " & characterHeight & " meters" & vbCrLf & _
"Force Power Level: " & forcePowerLevel & vbCrLf & _
"Credits: " & credits & vbCrLf & _
"Precise Calculation: " & preciseCalculation & vbCrLf & _
"Character Name: " & characterName & vbCrLf & _
"Is Jedi: " & isJedi & vbCrLf & _
"Birth Date: " & birthDate & vbCrLf & _
"Description: " & characterDescription
End Sub
Following these instructions will allow you to effectively run and interact with the VBA program, gaining a practical understanding of how various data types manage and display information:
To use the "Exploring VBA Data Types Through a Star Wars Character Example" program, follow these steps:
Open Excel and Access the VBA Editor:
Open Microsoft Excel.
Press
Alt + F11to open the VBA editor.
Insert a New Module:
In the VBA editor, click on
Insertin the menu bar.Select
Modulefrom the dropdown menu. This will create a new module where you can write your VBA code.
Copy and Paste the Code:
Copy the entire VBA code provided in the example.
Paste the code into the newly created module in the VBA editor.
Run the Program:
Ensure your cursor is within the
Sub StarWarsCharacterInfo()procedure.Press
F5or click on theRunbutton (green triangle) in the toolbar to execute the program.
View the Output:
- A message box will appear displaying the character information for Luke Skywalker, including attributes like rank, age, and force power level.
Explore and Modify:
Feel free to modify the variable values or add additional characters to explore how different data types can be used in VBA.
You can also add more message boxes or print statements to display additional information or test other data types.
My other related articles
Beginner's Guide to Customizing VBA: Code Editor Colors and More
Simplifying VBA Debugging: Real-Time Insights with Immediate and Locals Windows