Understanding Python Type Hierarchy
Python is a dynamically types language, which means that the type of a variable is determined at runtime. Understanding the type hierarchy in Python is crucial for writing efficient and error-free code. This article will provide a detailed yet easy to understand overview of Python's type hierarchy. Basic Types int: Represents integer values. float: Represents floating-point numbers. complex: Represents complex numbers. bool: Represents Boolean values(True or False), which is a subclass of int. str: Represents string values, which are sequences of characters. Sequence Types Sequence types are collections that maintain the order of their elements and allow for indexing and slicing: str: Immutable sequence of characters. list: An ordered, mutable collection of items. tuple: An ordered, immutable collection of items. range: Represents an immutable sequence of numbers, commonly used for looping a specific number of times in for loops. Set Types Set types are collections of unique items: set: An unordered collection of unique items. frozenset: An immutable version of a set. Mapping Types Mapping types are collections of key-value pairs: dict: A collection of key-value pairs. Special Types There are also some special types in Python: NoneType: Represents the absence of a value, with a single instance None. type: The type of all types, including itself. Other Built-in Types Python also includes several other built-in types: bytes: Represents immutable sequences of bytes. bytearray: Represents mutable sequences of bytes. memoryview: Provides a view of the memory of another binary object.
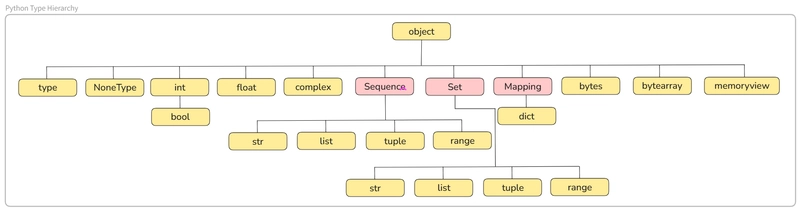
Python is a dynamically types language, which means that the type of a variable is determined at runtime. Understanding the type hierarchy in Python is crucial for writing efficient and error-free code. This article will provide a detailed yet easy to understand overview of Python's type hierarchy.
Basic Types
int: Represents integer values.
float: Represents floating-point numbers.
complex: Represents complex numbers.
bool: Represents Boolean values(True or False), which is a subclass of int.
str: Represents string values, which are sequences of characters.
Sequence Types
Sequence types are collections that maintain the order of their elements and allow for indexing and slicing:
str: Immutable sequence of characters.
list: An ordered, mutable collection of items.
tuple: An ordered, immutable collection of items.
range: Represents an immutable sequence of numbers, commonly used for looping a specific number of times in for loops.
Set Types
Set types are collections of unique items:
set: An unordered collection of unique items.
frozenset: An immutable version of a set.
Mapping Types
Mapping types are collections of key-value pairs:
- dict: A collection of key-value pairs.
Special Types
There are also some special types in Python:
NoneType: Represents the absence of a value, with a single instance None.
type: The type of all types, including itself.
Other Built-in Types
Python also includes several other built-in types:
bytes: Represents immutable sequences of bytes.
bytearray: Represents mutable sequences of bytes.
memoryview: Provides a view of the memory of another binary object.