Secure Coding Practices in Python
Use Secure Authentication and Authorization from passlib.hash import bcrypt password = "securepassword123" hashed_password = bcrypt.hash(password) print(bcrypt.verify("securepassword123", hashed_password)) # True Keep Dependencies and Frameworks Updated Use virtual environments and keep dependencies updated Run: pip install --upgrade pip && pip list --outdated Implement Proper Error Handling and Logging import logging logging.basicConfig(filename='app.log', level=logging.INFO) def divide(a, b): try: return a / b except ZeroDivisionError as e: logging.error("Division by zero attempted: %s", e) return None print(divide(10, 0)) # Logs the error Secure Data Transmission and Storage from cryptography.fernet import Fernet key = Fernet.generate_key() cipher_suite = Fernet(key) data = b"Sensitive Information" encrypted_data = cipher_suite.encrypt(data) decrypted_data = cipher_suite.decrypt(encrypted_data) print(decrypted_data.decode()) # Outputs original data Conclusion By following these secure coding practices in Python, developers can build more attack-resistant applications. Implementing input validation, secure authentication, proper error handling, dependency management, and encryption techniques will help secure your applications against common vulnerabilities. Stay aware, keep learning, and always prioritize security!

Use Secure Authentication and Authorization
from passlib.hash import bcrypt
password = "securepassword123"
hashed_password = bcrypt.hash(password)
print(bcrypt.verify("securepassword123", hashed_password)) # True
Keep Dependencies and Frameworks Updated
Use virtual environments and keep dependencies updated
Run: pip install --upgrade pip && pip list --outdated
Implement Proper Error Handling and Logging
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='app.log', level=logging.INFO)
def divide(a, b):
try:
return a / b
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
logging.error("Division by zero attempted: %s", e)
return None
print(divide(10, 0)) # Logs the error
Secure Data Transmission and Storage
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
key = Fernet.generate_key()
cipher_suite = Fernet(key)
data = b"Sensitive Information"
encrypted_data = cipher_suite.encrypt(data)
decrypted_data = cipher_suite.decrypt(encrypted_data)
print(decrypted_data.decode()) # Outputs original data
Conclusion
By following these secure coding practices in Python, developers can build more attack-resistant applications. Implementing input validation, secure authentication, proper error handling, dependency management, and encryption techniques will help secure your applications against common vulnerabilities. Stay aware, keep learning, and always prioritize security!
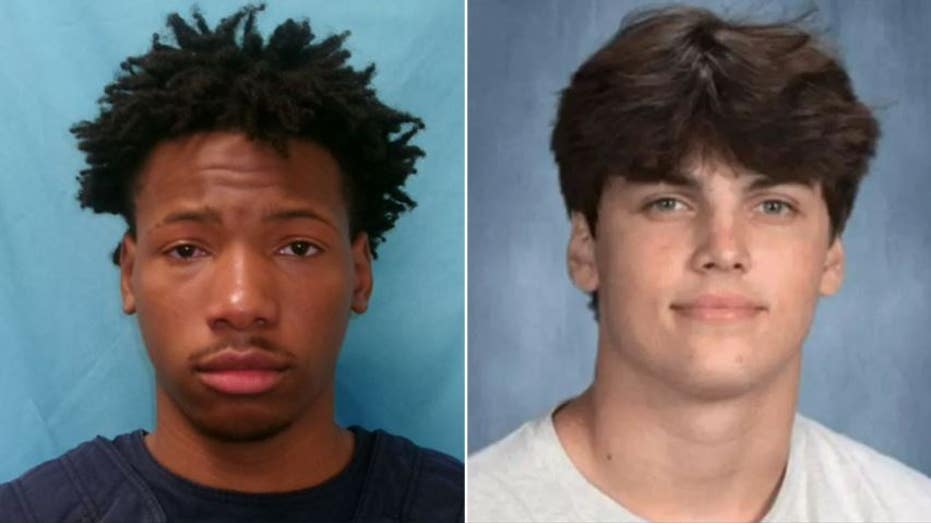
















_Igor_Mojzes_Alamy.jpg?#)

























































